


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 25-4-2017
Date: 1-1-2021
Date: 26-3-2017
|
Liquid Drop Model of a Nucleus
The nucleus is held together by the attractive nuclear force between nucleons, which was discussed in a previous chapter. The characteristics of the nuclear force are listed below.
(a) very short range, with essentially no effect beyond nuclear dimensions (∼10-13 cm)
(b) stronger than the repulsive electrostatic forces within the nucleus
(c) independent of nucleon pairing, in that the attractive forces between pairs of neutrons are no different than those between pairs of protons or a neutron and a proton
(d) saturable, that is, a nucleon can attract only a few of its nearest neighbors
One theory of fission considers the fissioning of a nucleus similar in some respects to the splitting of a liquid drop. This analogy is justifiable to some extent by the fact that a liquid drop is held together by molecular forces that tend to make the drop spherical in shape and that try to resist any deformation in the same manner as nuclear forces are assumed to hold the nucleus together.
By considering the nucleus as a liquid drop, the fission process can be described. Referring to Figure 1(A), the nucleus in the ground state is undistorted, and its attractive nuclear forces are greater than the repulsive electrostatic forces between the protons within the nucleus. When an incident particle (in this instance a neutron) is absorbed by the target nucleus, a compound nucleus is formed. The compound nucleus temporarily contains all the charge and mass involved in the reaction and exists in an excited state. The excitation energy added to the compound nucleus is equal to the binding energy contributed by the incident particle plus the kinetic energy possessed by that particle. Figure 1(B) illustrates the excitation energy thus imparted to the compound nucleus, which may cause it to oscillate and become distorted. If the excitation energy is greater than a certain critical energy, the oscillations may cause the compound nucleus to become dumbbell-shaped. When this happens, the attractive nuclear forces (short-range) in the neck area are small due to saturation, while the repulsive electrostatic forces (long-range) are only slightly less than before. When the repulsive electrostatic forces exceed the attractive nuclear forces, nuclear fission occurs, as illustrated in Figure 1(C).
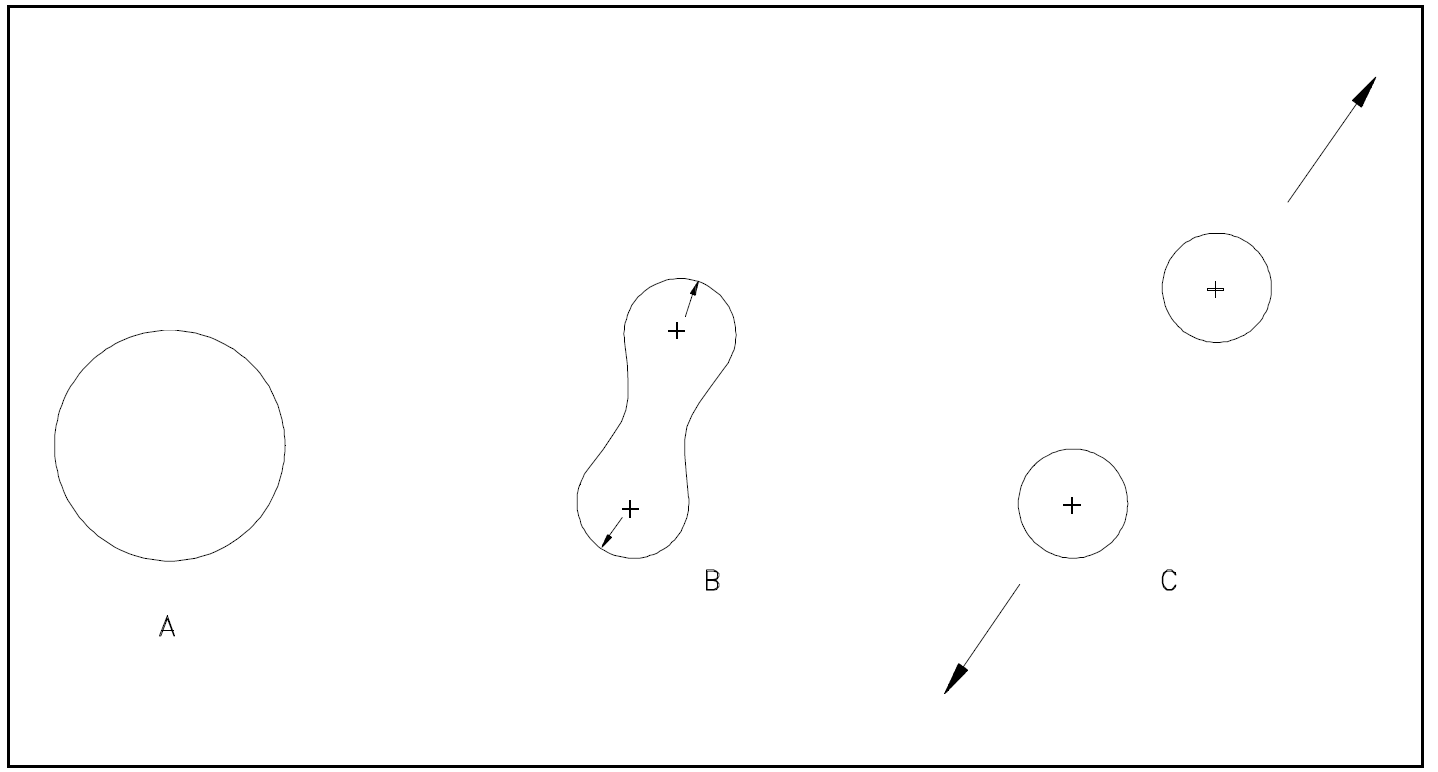
Figure 1: Liquid Drop Model of Fission



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|