


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 23-1-2021
Date: 22-12-2020
Date: 21-12-2020
|
Ion-exchange Chromatography (IEX)
Ion-exchange chromatography is the most commonly used chromatographic step in downstream bioprocessing and is an adsorptive binding and elute method. Ion exchange can be subdivided into cation exchange, whereby positively charge molecules bind, and anion exchange, whereby negatively charged molecules bind the resin. In both cases, the bound material is usually eluted by increasing the salt concentration.
The target protein of interest must therefore be in a buffer of the appropriate pH and salt concentration before being applied to the column. As outlined in Table .1, commonly used ligands include carboxymethyl and diethylaminoethyl (DEAE) for cation and anion exchange, respectively.
Table .1 Details of the four major chromatographic methods used for downstream processing of biologics.

Further, as can be seen in Figure 1, ion exchange dominates as the method of choice in most steps due to the fact it is used as a bulk purification method and a polishing step and the fact that a weak binding high capacity ion-exchange step is followed by a lower capacity strong affinity binding step.
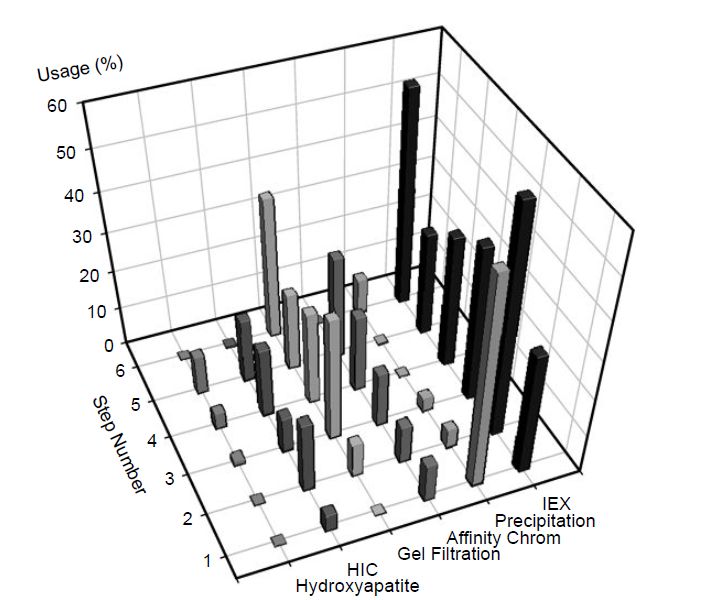
Figure 1 The use of chromatography and precipitation methods as a percentage of the total number of unit operations at a given step throughout downstream processing as determined from a survey of the primary literature. IEX, ion exchange; HIC, hydrophobic interaction chromatography.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|