


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 18-8-2020
التاريخ: 18-3-2019
التاريخ: 2-8-2016
التاريخ: 16-11-2019
|
What is a cell ?
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
Cells have many parts, each with a different function. Some of these parts, called organelles, are specialized structures that perform certain tasks within the cell. Human cells contain the following major parts, listed in alphabetical order:
Cytoplasm
Within cells, the cytoplasm (image on page 7) is made up of a jelly-like fluid (called the cytosol) and other structures that surround the nucleus.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a network of long fibers that make up the cell’s structural framework. The cytoskeleton has several critical functions, including determining cell shape, participating in cell division, and allowing cells to move. It also provides a track-like system that directs the movement of organelles and other substances within cells.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
This organelle helps process molecules created by the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum (image on page 7) also transports these molecules to their specific destinations either inside or outside the cell.
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (image on page 8) packages molecules processed by the endoplasmic reticulum to be transported out of the cell.
Lysosomes and peroxisomes
These organelles (image on page 8) are the recycling center of the cell. They digest foreign bacteria that invade the cell, rid the cell of toxic substances, and recycle worn-out cell components.
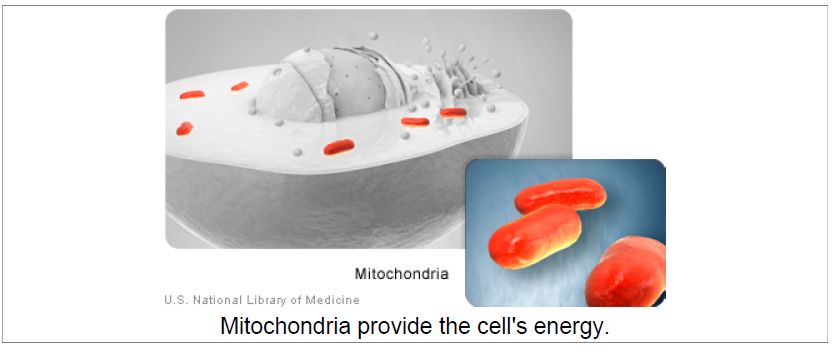
Mitochondria
Mitochondria (image on page 8) are complex organelles that convert energy from food into a form that the cell can use. They have their own genetic material, separate from the DNA in the nucleus, and can make copies of themselves.
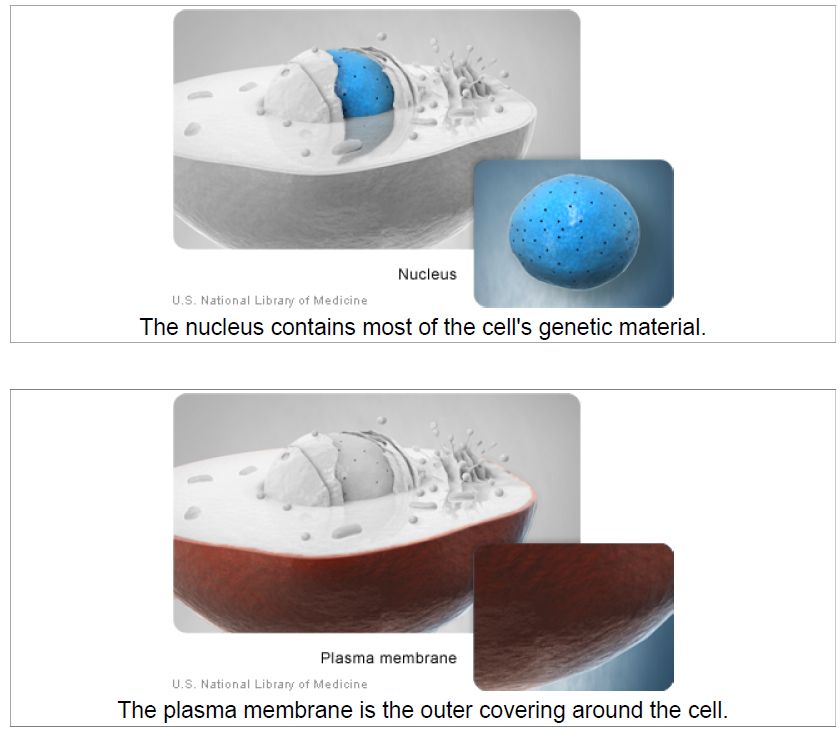
Nucleus
The nucleus (image on page 9) serves as the cell’s command center, sending directions to the cell to grow, mature, divide, or die. It also houses DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the cell’s hereditary material. The nucleus is surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope, which protects the DNA and separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell.
Plasma membrane
The plasma membrane (image on page 9) is the outer lining of the cell. It separates the cell from its environment and allows materials to enter and leave the cell.
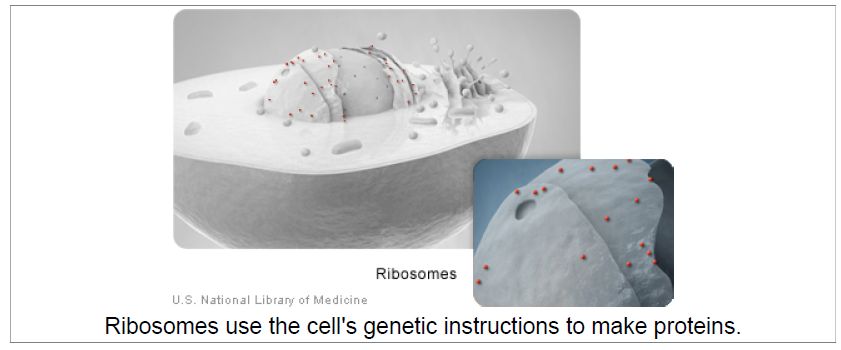
Ribosomes
Ribosomes (image on page 9) are organelles that process the cell’s genetic instructions to create proteins. These organelles can float freely in the cytoplasm or be connected to the endoplasmic reticulum .





|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
خدمات متعددة يقدمها قسم الشؤون الخدمية للزائرين
|
|
|