


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 20-5-2017
Date: 8-5-2017
Date: 20-5-2017
|
Conductivity
The drift current density, may be written as
 (1)
(1)
where σ is the conductivity of the semiconductor material. The conductivity is giver in units of (Ω-cm)-1 and is a function of the electron and hole concentrations and mobilities. We have just seen that the mobilities are functions of impurity concentration, conductivity, then is a somewhat complicated function of impurity concentration.
The reciprocal of conductivity is resistivity, which is denoted by ρ and is giver in units of ohm-cm. We can write the formula for resistivity as
 (2)
(2)
Figure 1.1 is a plot of resistivity as a function of impurity concentration in silicon germanium, gallium arsenide, and gallium phosphide at T = 300 K. Obviously, the curves are not linear functions of Nd or Na because of mobility effects.
If we have a bar of semiconductor material as shown in Figure 1.2 with a volt age applied that produces a current I, then we can write
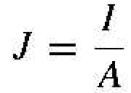 (3a)
(3a)
and
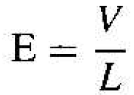 (3b)
(3b)

Figure 1.1 Resistivity versus impurity concentration at T = 300 K in (a) silicon and (b) germanium, gallium arsenide, and gallium phosphide.
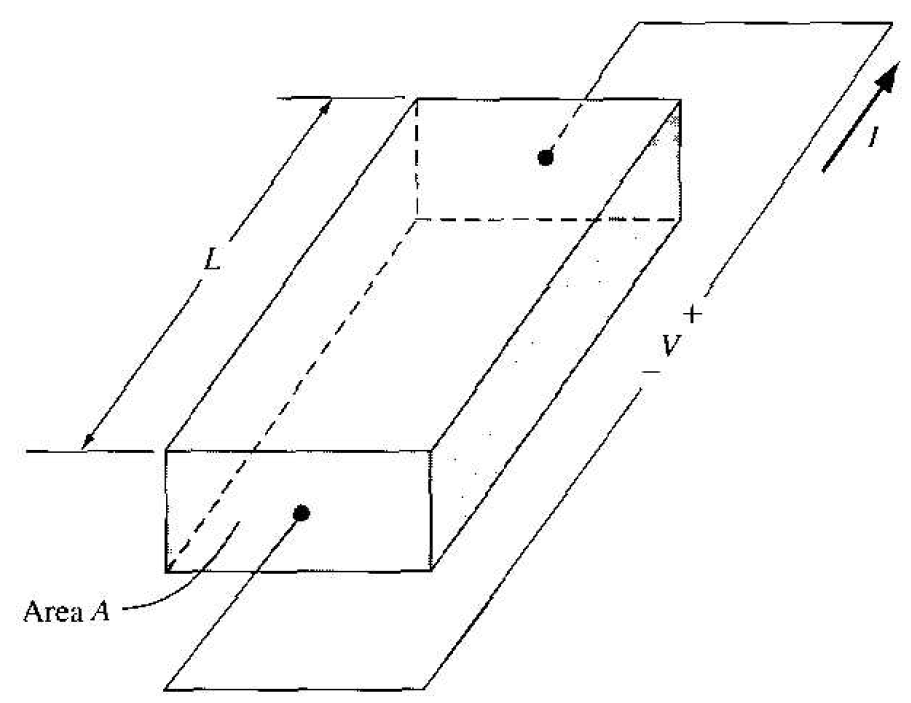
Figure 1.2 Bar of semiconductor material as a resistor.
We can now rewrite Equation (1) as
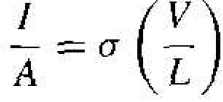 (4)
(4)
or
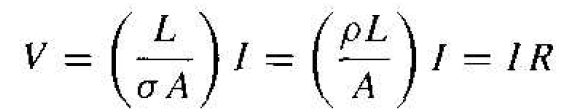 (5)
(5)
Equation (3b) is Ohm's law for a semiconductor. The resistance is a function of resistivity, or conductivity, as well as the geometry of the semiconductor.
If we consider. for example, a p-type semiconductor with an acceptor doping Na(Nd = 0) in which Na >> ni , and if we assume that the electron and hole mobilities are of the same order of magnitude, then the conductivity becomes
 (6)
(6)
If we also assume complete ionization, then Equation (6) becomes
 (7)
(7)
The conductivity and resistivity of an extrinsic semiconductor are a function primarily of the majority carrier parameters.
We may plot the carrier concentration and conductivity of a semiconductor as a function of temperature for a particular doping concentration. Figure 1.3 shows the electron concentration and conductivity of silicon as a function of inverse temperature for the case when Nd = 1015 cm-3. In the midtemperature range, or extrinsic range, as shown, we have complete ionization-the electron concentration remains essentially constant. However, the mobility is a function of temperature so the conductivity
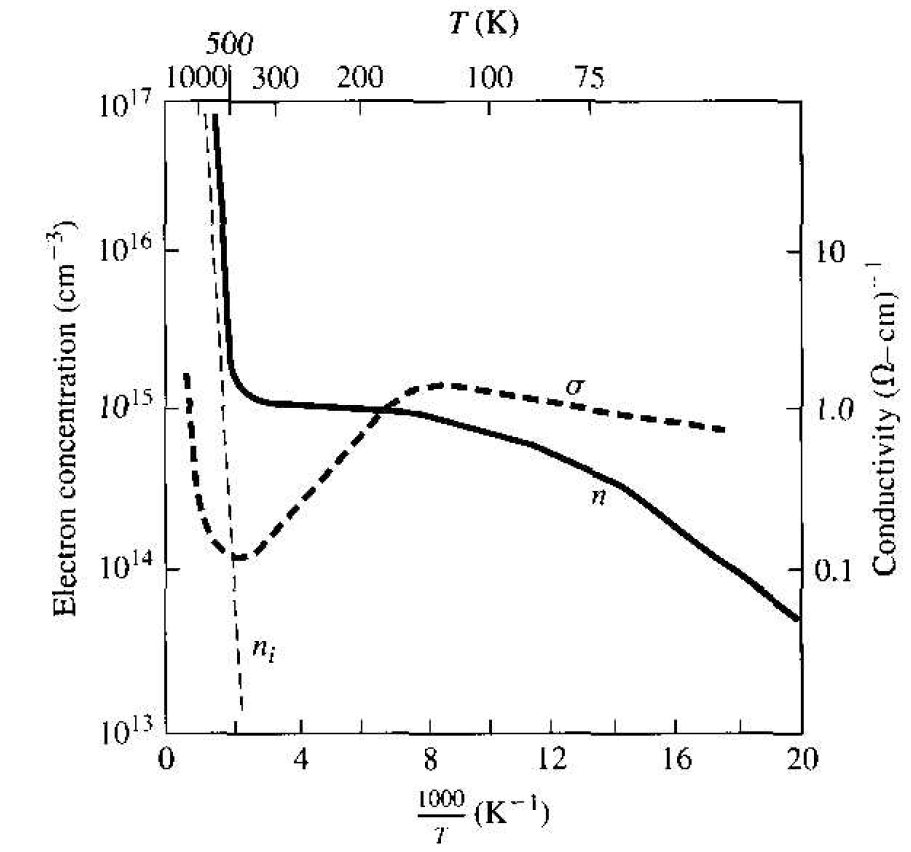
Figure 1.3 Electron concentration and conductivity versus inverse temperature for silicon.
varies with temperature in this range. At higher temperatures, the intrinsic cattier concentration increases and begins to dominate the electron concentration as well as the conductivity. In the lower temperature range, freeze-out begins to occur; the electron concentration and conductivity decrease with decreasing temperature.
For an intrinsic material, the conductivity can be written as
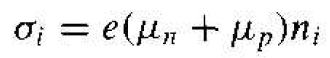 (8)
(8)
The concentrations of electrons and holes are equal in an intrinsic semiconductor, so the intrinsic conductivity includes both the electron and hole mobility. Since, in general, the electron and hole mobilities are not equal, the intrinsic conductivity is not the minimum value possible at a given temperature.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|