


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 20-5-2017
Date: 14-5-2017
Date: 8-5-2017
|
Diffusion Current Density
To begin to understand the diffusion process in a semiconductor, we will consider simplified analysis. Assume that an electron concentration varies in one dimension shown in Figure 1.1. The temperature is assumed to be uniform so that the average thermal velocity of electrons is independent of x. To calculate the current, we will determine the net Row of electrons per unit time per unit area crossing the plane a x = 0. If the distance l shown in Figure 1.1 is the mean-free path of an electron, this is, the average distance an electron travels between collisions (l = vth τcn), then on the average, electrons moving to the right at x = -l and electrons moving to the at x = +l will cross the x = 0 plane. One half of the electrons at x = -l will be traveling to the right at any instant of time and one half of the electrons at x = +l will be traveling to the left at any given time. The net rate of electron flow, Fn, in the +l
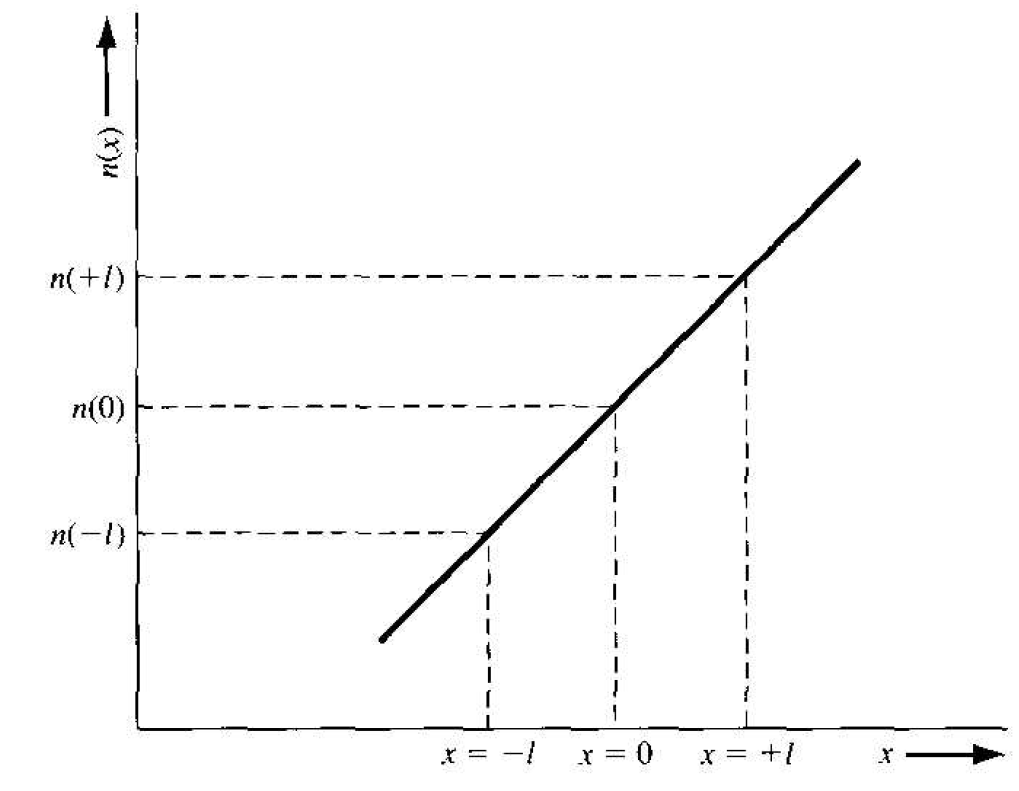
Figure 1.2 Electron concentration versus distance.
direction at x = 0 is given by
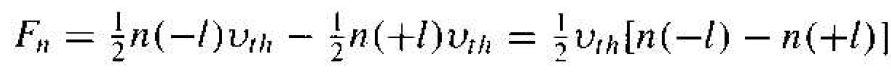 (1)
(1)
If we expand the electron concentration in a Taylor series about x = 0 keeping only the first two terms, then we can write Equation (1) as
 (2)
(2)
which becomes
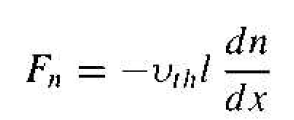 (3)
(3)
Each electron has a charge (-e), so the current is
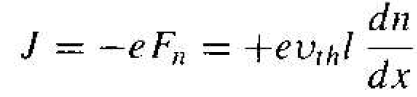 (4)
(4)
The current described by Equation (4) is the electron diffusion current and is proportional to the spatial derivative, or density gradient, of the electron concentration. The diffusion of electrons from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration produces a flux of electrons flowing in the negative x direction for this example. Since electrons have a negative charge, the conventional current direction is in the positive x direction. Figure 1.2a shows these one-dimensional flux and current directions. We may write the electron diffusion current density for this one dimensional case. in the form
 (5)
(5)
where Dn is called the electron diffusion coefficient, has units of cm2/s, and is a positive quantity. If the electron density gradient becomes negative, the electron diffusion current density will be in the negative x direction.
Figure 1.2b shows an example of a hole concentration as a function of distance in a semiconductor. The diffusion of holes, from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration, produces a flux of holes in the negative x direction. Since holes are positively charged particles, the conventional diffusion current density is also in the negative x direction. The hole diffusion current density is proportional to the hole density gradient and to the electronic charge, so we may write
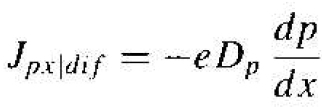 (6)
(6)

Figure 1.2 (a) Diffusion of electrons due to a density gradient. (b) Diffusion of holes due to a density gradient.
for the one-dimensional case. The parameter Dp is called the hole diffusion coefficient, has units of cm2/s, and is a positive quantity. If the hole density gradient becomes negative, the hole diffusion current density will be in the positive x directed.



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مشاتل الكفيل تزيّن مجمّع أبي الفضل العبّاس (عليه السلام) بالورد استعدادًا لحفل التخرج المركزي
|
|
|