


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 31-7-2016
Date: 8-1-2017
Date: 10-1-2017
|
Mitochondria
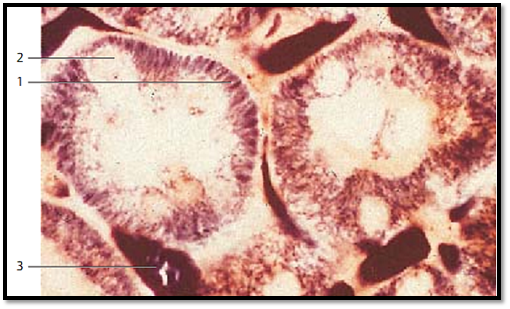
Before the turn of the 19th century, Altmann discovered and described mitochondria, the power plant organelle of cells, as granular, rod-like stringy cell components. In 189 8, C. Benda introduced the term mitochondria for these “threaded bodies” (mitos, Greek: thread; chondros, Greek: granulum). Later (1952–1953), electron microscopy made it possible for G. E. Palade and F. S. Sjöstrand to show the characteristic structural details of mitochondria. This figure shows mitochondria 1 in the epithelial cells of renal tubules. The mitochondria stand out as long, black-brown rods, which line up in the basal cytoplasm to almost parallel rows. The cell nuclei 2 are not visible; their positions appear as gaps.
1 Mitochondria in the form of short rods
2 Epithelial cell nuclei
3 Blood vessels
The basic structure follows the same principle layout in all mitochondria. An outer membrane ( outer mitochondrial membrane) separates the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm. Inside this outer membrane (border) lies the inner membrane. It forms septum-like folds ( cristae mitochondriales), which ex-tend to various lengths across the organelle ( crista-type mitochondria). The inner and outer membranes separate two cell compartments. Between the outer and inner membrane, separated by about 8 nm, lies the outer compartment ( outer metabolic compartment, intermembrane space), which extends into the crevices of the cristae. The inner membrane and its cristae forms the border around the inner compartment (inner metabolic space). It contains a homogeneous or granular matrix of variable density. The inner mitochondrial matrix of ten contains granules, the granula mitochondrialia or matrix granules, which have a size of 30–50 nm and are rich in Ca2+ and other ions.
This picture shows mitochondria from a heart muscle cell.
1 Myofilament bundles of the striated hear t muscle cell

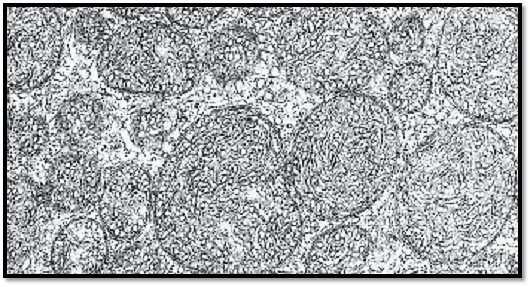
Sizes and shapes of mitochondria can be very different. On average, they are 0.25 μm thick and 2–7 μm long. Nevertheless, there are also giant forms (giant mitochondria). The numb er of cristae mitochondriales also varies. As a result, the sizes of the inner and outer compartments are also different. The figure shows mitochondria (crista-type) in a cell from the mucosal stomach lining, which have been cut in different planes. Note the granula mitochondrialia, with diameters between 30–50 nm in the matrix (matrix granules ).

Pre dominantly oval, crista-type mitochondria from an epithelial cell of a proximal kidney tubule. The folds that originate at the inner membranes and extend into the inner centers of the mitochondria—the cristae mitochondrial—are different in length and form a series of incomplete transverse septa. Note the osmiophilic granula mitochondrial in the matrix. Some of the mitochondria are cut tangentially, and their cristae therefore appear diffuse, or are not discernible at all. Between the mitochondria are the basal plasmalemma folds.

Oval-shaped, often arcuate, crista-type mitochondria with an electron-dense (osmiophilic) matrix are lined up alongside the inner cell membranes at the border between two cells (intercellular space) 1 . Note the interdigitations 1 between neighboring gland cells. Gland cells with secretory granules 2 from the human lacrimal gland (glandula lacrimalis).
1 Intercellular space with interdigitations
2 Secretor y granules
↑ Cont act between cells (desmosome)

Apart from crista-type mitochondria, there are also mitochondria with inner membranes, which protrude into the mitochondrion like f ingers or sacs 1 . These are tubular or saccular-type mitochondria. The processes can also be rod-like or have edges, as they do in prismatic-type mitochondria. Tubular and saccular-type mitochondria occur in steroid hormone-producing cells. The figure shows oval, slender mitochondria in cells from the adrenal cortex. Their tubules are mostly cut in rectangular direction. They are visually empty. Note the dense mitochondrial matrix and the light space between the outer and inner membranes. Between the mitochondria are smooth ER membranes and ribosomes.
1 Tubuli mitochondriales, cut lengthwise
2 Lipid vacuole
3 Cell nucleus, cut tangentially
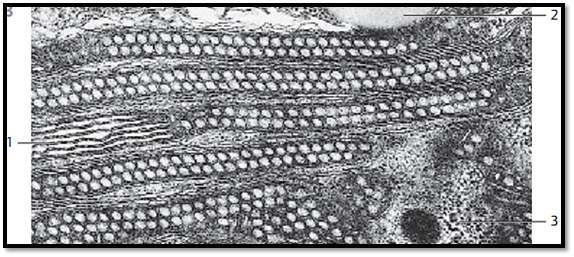
Tubular -type mitochondria in an adrenal cortex cell from the zona fasciculata . Winding tubules extend from the inner mitochondrial membrane. They are cut at different angles along their winding paths. The result is a section with a variety of profiles.
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgar t · New York .



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|