


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 29-12-2015
Date: 5-4-2021
Date: 25-12-2015
|
Glutaraldehyde
The bis-homobifunctional aldehyde glutaraldehyde
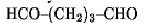
is perhaps the most frequently used chemical crosslinking agent. Because of its effectiveness as a crosslinker, glutaraldehyde has found use as a stabilizer or fixative for samples subjected to electron microscopy, for bioprosthetic materials, and in drug delivery systems. It is also routinely used to produce bioconjugates and to immobilize proteins.
Crosslinking by glutaraldehyde can occur through at least two distinct mechanisms (2). The first is attack by primary amino groups of the protein on the aldehydic carbons of glutaraldehyde to form Schiff bases, which can then be rendered irreversible by suitable reductants. The second mechanism is more complex and less understood, and it results in irreversible crosslinking in the absence of reductants. This alternative mechanism involves polymerization of glutaraldehyde to form heterogeneous unsaturated polymers that differ in their length and degree of unsaturation. These polymers then undergo addition at their double bonds by other nucleophilic groups of the protein. A disadvantage of glutaraldehyde is that it often brings about extensive crosslinking and formation of insoluble complexes; however, this can be minimized through use of the two-step reaction, in which one protein is reacted with glutaraldehyde, the excess reagent removed, and the second protein then added to react with the free aldehyde groups of the first (2).
References
1. A. Jayakrishnan and S. R. Jameela (1996) Biomaterials 17, 471–484.
2. G. T. Hermanson (1996) Bioconjugate Techniques, Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 218–220.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|