


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 31-5-2017
Date: 10-5-2019
Date: 12-9-2019
|
Noncovalent Interactions between Molecules
When thinking about chemical reactivity, chemists usually focus their attention on bonds, the covalent interactions between atoms within molecules. Also important, however, particularly in large biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids, are a variety of interactions between molecules that strongly affect molecular properties. Collectively called either intermolecular forces, van der Waals forces, or noncovalent interactions, they are of several different types: dipole–dipole forces, dispersion forces, and hydrogen bonds. Dipole–dipole forces occur between polar molecules as a result of electrostatic interactions among dipoles. The forces can be either attractive or repulsive depending on the orientation of the molecules—attractive when unlike charges are together and repulsive when like charges are together. The attractive geometry is lower in energy and therefore predominates (Figure 1).
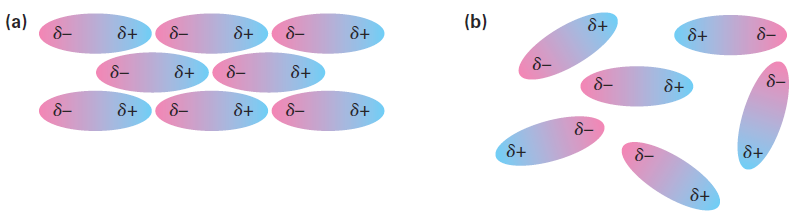
Figure 1 . Dipole–dipole forces cause polar molecules (a) to attract one another when they orient with unlike charges together, but (b) to repel one another when they orient with like charges together.
Dispersion forces occur between all neighboring molecules and arise because the electron distribution within molecules is constantly changing.
Although uniform on a time-averaged basis, the electron distribution even in nonpolar molecules is likely to be nonuniform at any given instant. One side of a molecule may, by chance, have a slight excess of electrons relative to the opposite side, giving the molecule a temporary dipole. This temporary dipole in one molecule causes a nearby molecule to adopt a temporarily opposite dipole, resulting in a tiny attraction between the two (Figure 2.). Temporary molecular dipoles have only a fleeting existence and are constantly changing, but their cumulative effect is often strong enough to hold molecules close together so that a substance is a liquid or solid rather than a gas.

Figure 2. Attractive dispersion forces in nonpolar molecules are caused by temporary dipoles, as shown in these models of pentane, C5H12.
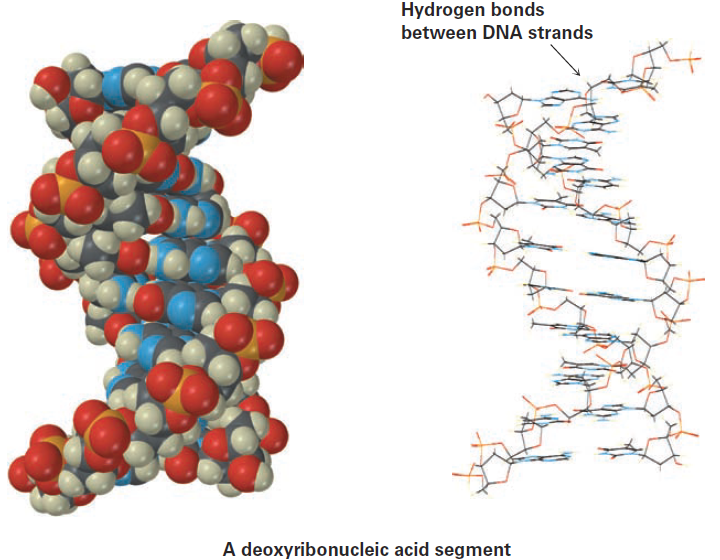
Perhaps the most important noncovalent interaction in biological molecules is the hydrogen bond, an attractive interaction between a hydrogen bonded to an electronegative O or N atom and an unshared electron pair on another O or N atom. In essence, a hydrogen bond is a very strong dipole–dipole interaction involving polarized O-H or N-H bonds. Electrostatic potential maps of water and ammonia clearly show the positively polarized hydrogens (blue) and the negatively polarized oxygens and nitrogens (red).

Hydrogen bonding has enormous consequences for living organisms. Hydrogen bonds cause water to be a liquid rather than a gas at ordinary temperatures, they hold enzymes in the shapes necessary for catalyzing biological reactions, and they cause strands of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) to pair up and coil into the double helix that stores genetic information.
One further point before leaving the subject of noncovalent interactions: biochemists frequently use the term hydrophilic, meaning “water-loving,” to describe a substance that is strongly attracted to water and the term hydrophobic, meaning “water-fearing,” to describe a substance that is not strongly attracted to water. Hydrophilic substances, such as table sugar, usually have a number of ionic charges or polar -OH groups in their structure so they can form hydrogen bonds, whereas hydrophobic substances, such as vegetable oil, do not have groups that form hydrogen bonds, so their attraction to water is limited to weak dispersion forces.



|
|
|
|
لمكافحة الاكتئاب.. عليك بالمشي يوميا هذه المسافة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تحذيرات من ثوران بركاني هائل قد يفاجئ العالم قريبا
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية تشارك في معرض النجف الأشرف الدولي للتسوق الشامل
|
|
|