


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 16-10-2020
Date: 2-1-2017
Date: 20-12-2020
|
FLUX DENSITY VERSUS CURRENT
In a straight wire carrying a steady direct current surrounded by air or by free space (a vacuum), the flux density is greatest near the wire and diminishes with increasing distance from the wire. You ask, “Is there a formula that expresses flux density as a function of distance from the wire?” The answer is yes. Like all formulas in physics, it is perfectly accurate only under idealized circumstances.
Consider a wire that is perfectly thin, as well as perfectly straight. Suppose that it carries a current of I amperes. Let the flux density (in teslas) be denoted B. Consider a point P at a distance r (in meters) from the wire, as measured along the shortest possible route (that is, within a plane perpendicular to the wire). This is illustrated in Fig. 1. The following formula applies:
B = 2 × 10-7 (I/r)
In this formula, the value 2 can be considered mathematically exact to any desired number of significant figures.
As long as the thickness of the wire is small compared with the distance r from it, and as long as the wire is reasonably straight in the vicinity of the point P at which the flux density is measured, this formula is a good indicator of what happens in real life.
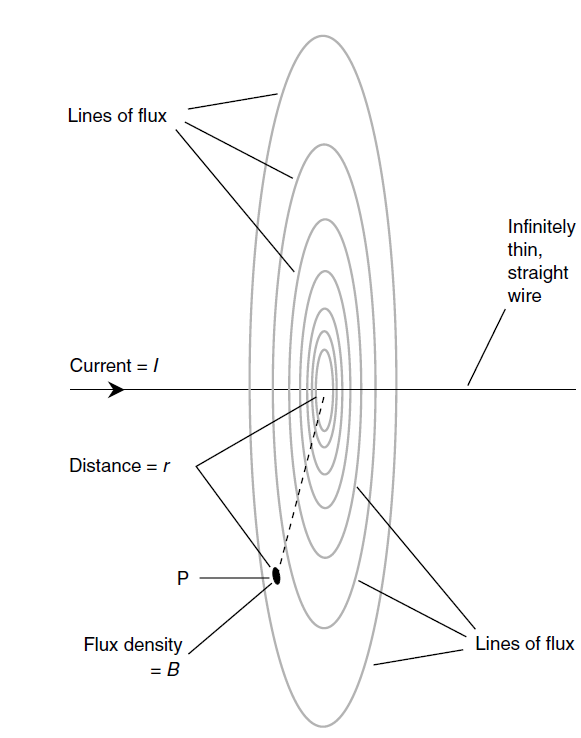
Fig. 1. Flux density varies inversely with the distance from a wire carrying direct current.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|