


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 16-5-2017
Date: 30-6-2019
Date: 12-7-2018
|
Addition to a carbonyl by a semi-anionic hydride, such as NaBH4, results in conversion of the carbonyl compound to an alcohol. The hydride from the BH4- anion acts as a nucleophile, adding H- to the carbonyl carbon. A proton source can then protonate the oxygen of the resulting alkoxide ion, forming an alcohol.
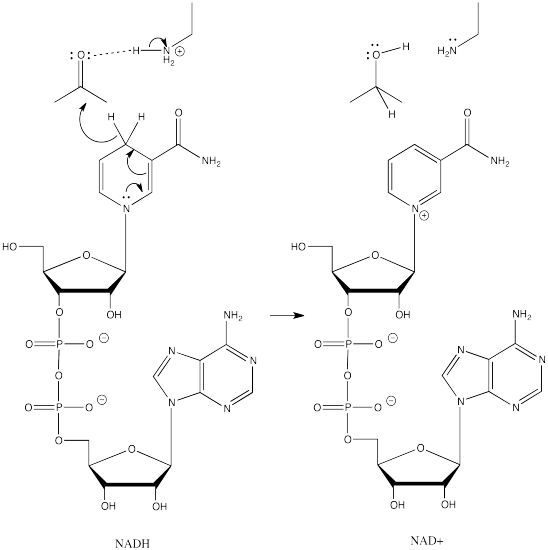
Formally, that process is referred to as a reduction. Reduction generally means a reaction in which electrons are added to a compound; the compound that gains electrons is said to be reduced. Because hydride can be thought of as a proton plus two electrons, we can think of conversion of a ketone or an aldehyde to an alcohol as a two-electron reduction. An aldehyde plus two electrons and two protons becomes an alcohol.
Aldehydes, ketones and alcohols are very common features in biological molecules. Converting between these compounds is a frequent event in many biological pathways. However, semi-anionic compounds like sodium borohydride don't exist in the cell. Instead, a number of biological hydride donors play a similar role.
NADH is a common biological reducing agent. NADH is an acronym for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydride. Insetad of an anionic donor that provides a hydride to a carbonyl, NADH is actually a neutral donor. It supplies a hydride to the carbonyl under very specific circumstances. In doing so, it forms a cation, NAD+. However, NAD+ is stabilized by the fact that its nicotinamide ring is aromatic; it was not aromatic in NADH.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|