
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Inclined Plane with Friction
المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
المصدر:
Physics 2000
الجزء والصفحة:
273
24-11-2020
2651
Inclined Plane with Friction
In our analysis of the air cart on the inclined track, we mentioned that a frictionless surface exerts only a normal force on an object. If there is any sideways force, that is supposed to be a friction force 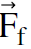 . In Figure (1) we show a cart on an inclined plane, with a friction force
. In Figure (1) we show a cart on an inclined plane, with a friction force 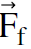 included. The normal force
included. The normal force 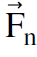 is perpendicular to the plane, the friction force
is perpendicular to the plane, the friction force 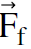 is parallel to the plane, and gravity still points down.
is parallel to the plane, and gravity still points down.
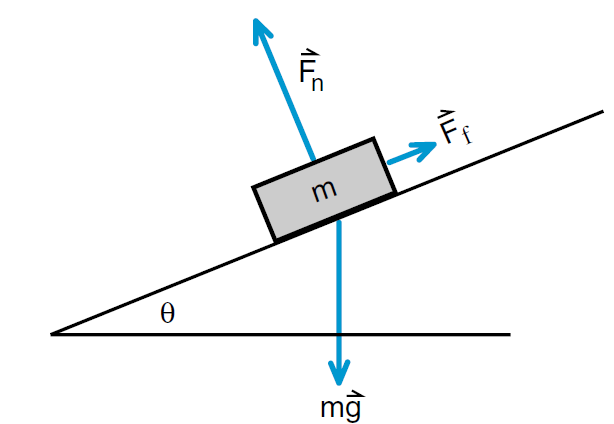
Figure 1: Friction force acting on the cart.
To analyze the motion of the cart when acted on by a friction force, we write Newton’s second law in the usual form
 ..........(1)
..........(1)
The only change is that we have added in the new force 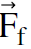 .
.
Since the motion of the cart is still along the plane, it is convenient to take the x axis along the plane as shown in Figure (2). Breaking Equation 1 up into x and y components now gives
 ...........(2a)
...........(2a)
 .........(2b)
.........(2b)
From 2b we get,
Fn = mg cos θ...........(3)
which is the same result as for the frictionless plane.
The new result comes when we look at motion down the plane. Solving 2a for ax gives
ax = gsinθ – Ff /m.......... (4)
Not surprisingly, the friction force reduces the acceleration down the plane.

Figure 2