


 1:29:46
1:29:46  2025-05-05
2025-05-05  1300
1300
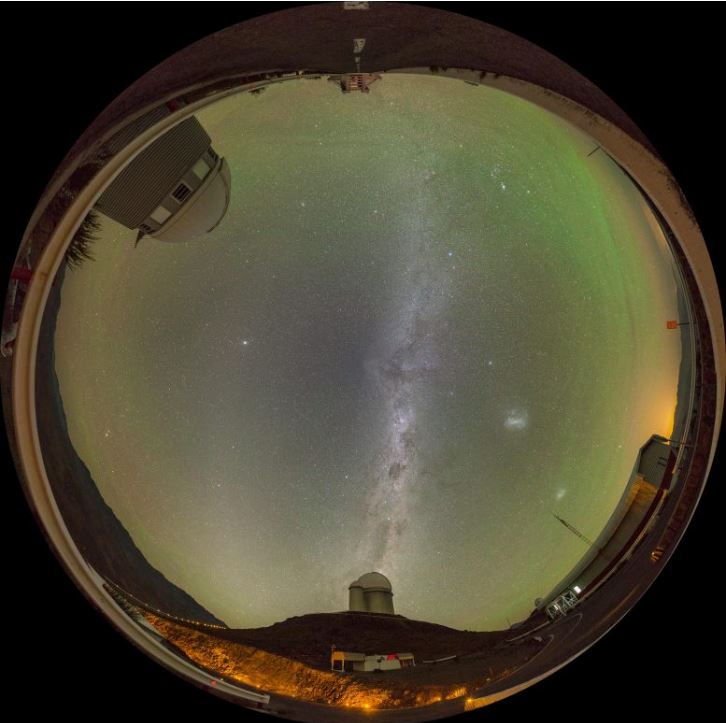

Hidden away in the darkest corners of Earth’s atmosphere, a faint green airglow quietly paints the night sky, far from the bustling interference of light pollution.
Captured above the La Silla Observatory in Chile’s Atacama Desert, this phenomenon is often confused with the more dramatic auroras but has its own mesmerizing, silent charm.
A Hidden Glow Above the Desert
The soft green glow filling the sky in this image is called airglow, a faint light naturally emitted by Earth’s upper atmosphere. Unlike the stars or auroras, you can’t see airglow with the naked eye. It’s far too dim. But in extremely dark locations, sensitive cameras can capture its ghostly presence. One such place is the La Silla Observatory, operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO), nestled on the edge of Chile’s remote Atacama Desert, where light pollution is almost nonexistent.
Airglow vs. Auroras: What’s the Difference?
Although airglow may look similar to the shimmering lights of an aurora, the two phenomena are quite different. Airglow is created when ultraviolet radiation from the Sun energizes atoms and molecules in the upper atmosphere. As these particles return to their normal state, they release faint light, producing a soft, steady glow.
Auroras, in contrast, are dramatic bursts of light triggered by charged particles from the Sun interacting with Earth’s magnetic field. Auroras are brief, unpredictable, and typically much brighter than airglow.
While airglow is ever-present in the night sky, it’s subtle—more like a gentle background hum than a fireworks show. The green color seen here comes from oxygen atoms, but airglow can also appear red or yellow, depending on the specific molecules involved.
A Telescope Treasure Hunt at La Silla
But there is more than just airglow hiding in this fisheye view of La Silla. Can you spot the three telescopes? ESO’s 3.6m telescope, at the bottom, is the one seemingly puffing the Milky Way like smoke. The Swiss 1.2-meter Leonhard Euler Telescope (top left) is also pretty easy to find, but the almost unrecognizable New Technology Telescope might be more of a challenge to find (it’s hiding at the top).
Now that you’ve found the telescopes, how about seeing them up close? Yes, you can actually visit them. There will be no airglow, as visits are during daytime to avoid interfering with the night-time work, and airglow is invisible to the naked eye – but the telescopes more than make up for it.
Reality Of Islam |
|
Stanford, C
A new study
Researchers
A new chip-
 9:3:43
9:3:43
 2018-11-05
2018-11-05
10 benefits of Marriage in Islam
 7:5:22
7:5:22
 2019-04-08
2019-04-08
benefits of reciting surat yunus, hud &
 9:45:7
9:45:7
 2018-12-24
2018-12-24
advantages & disadvantages of divorce
 11:35:12
11:35:12
 2018-06-10
2018-06-10
 6:0:51
6:0:51
 2018-10-16
2018-10-16
 8:39:51
8:39:51
 2022-09-23
2022-09-23
 10:35:40
10:35:40
 2022-05-26
2022-05-26
 9:39:36
9:39:36
 2022-12-28
2022-12-28
 10:43:56
10:43:56
 2022-06-22
2022-06-22
 7:32:24
7:32:24
 2022-02-14
2022-02-14
 9:30:2
9:30:2
 2021-11-12
2021-11-12
 11:2:27
11:2:27
 2022-10-06
2022-10-06
 5:41:46
5:41:46
 2023-03-18
2023-03-18
| LATEST |