
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
The Fermi-Dirac Probability Function
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
الجزء والصفحة:
p 89
17-5-2017
3521
The Fermi-Dirac Probability Function
Figure 1.1 shows the ith energy level with gi quantum states. A maximum of one particle is allowed in each quantum state by the Pauli exclusion principle. There are gi ways of choosing where to place the first panicle, (gi - 1 ) ways of choosing where to place the second particle, (gi - 2) ways of choosing where to place the third particle, and so on. Then the total number of ways of arranging Ni particles in the ith energy level (where Ni ≤ gi) is
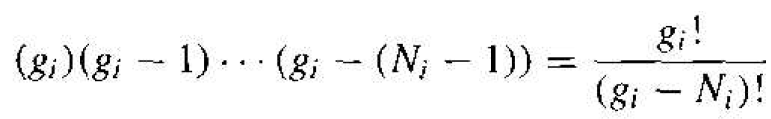 (1)
(1)
This expression includes all permutations of the Ni particles among themselves.
However, since the particles are indistinguishable, the Ni ! number of permutations that the particles have among themselves in any given arrangement do not count as separate arrangements. The interchange of any two electrons. for example, does not produce a new arrangement. Therefore, the actual number of independent ways of realizing a distribution of Ni particles in the ith level is
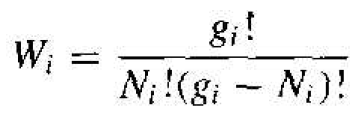 (2)
(2)

Figure 1.1 The ith energy level with gi quantum state.
Equation (2) gives the number of independent ways of realizing a distribution of Ni particles in the ith level. The total number of ways of arranging (N1, N2, N3, . . . , Nn) indistinguishable particles among n energy levels is the product of all distributions, or
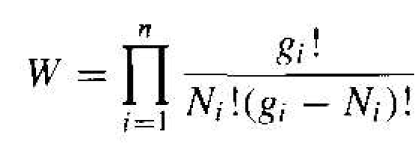 (3)
(3)
The parameter W is the total number of ways in which N electrons can be arranged in this system, where 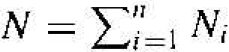 is the total number of electrons in the system. We want to find the most probable distribution, which means that we want to find the maximum W. The maximum W is found by varying Ni among the Ei levels, which vanes the distribution, but at the same time, we will keep the total number of particles and total energy constant.
is the total number of electrons in the system. We want to find the most probable distribution, which means that we want to find the maximum W. The maximum W is found by varying Ni among the Ei levels, which vanes the distribution, but at the same time, we will keep the total number of particles and total energy constant.
We may write the most probable distribution function as
 (4)
(4)
where EF is called the Fermi energy. The number density N (E) is the number of particles per unit volume per unit energy and the function g (E) is the number of quantum states per unit volume per unit energy. The function fF (E) is called the Fermi-Dirac distribution or probability function and gives the probability that a quantum state at the energy E will be occupied by an electron. Another interpretation of the distribution function is that fF (E) is the ratio of filled to total quantum states at any energy E.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















