
Venting
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 16
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 16
 10-9-2016
10-9-2016
 2029
2029
Venting
A thermally insulated chamber is pumped down to a very low pressure. At some point, the chamber is vented so that it is filled with air up to atmospheric pressure, whereupon the valve is closed. The temperature of the air surrounding the chamber is T0 = 300K What is the temperature T of the gas in the chamber immediately after venting?
SOLUTION
The air surrounding the chamber may be thought of as a very large reservoir of gas at a constant pressure P0 and temperature T0. The process of venting is adiabatic, so we can assume that there is no energy dissipation. We then find that the energy of the gas admitted to the chamber equals the sum of its energy E0 in the reservoir plus the work done by the gas of the reservoir at P0 to expel the gas into the chamber. This may be calculated by considering the process of filling a cylinder by pushing a piston back, where the piston offers a resistant force of P0A, A being the cross section of the cylinder. The total energy E is then given by
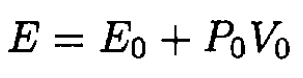 (1)
(1)

Figure 1.1
where V0 is the volume of the gas needed to fill the volume of the chamber V (note that V does not coincide with V0 because the temperature of the gas in the chamber T presumably is not the same as T0, see Figure 1.1). On the other hand.
 (2)
(2)
where CV is the heat capacity of the gas, cv is the heat capacity per molecule, and N0 is the number of molecules. From (1) and (2), we have
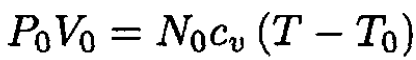 (3)
(3)
Using the ideal gas law
 (4)
(4)
we have
 (5)
(5)
So
 (6)
(6)
The air is mostly nitrogen and oxygen (78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen = 99%), diatomic gases, so that
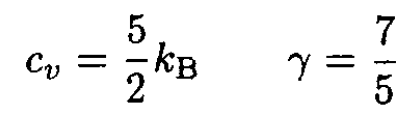
and therefore T = 240 K. Thus, the temperature of the gas in the chamber will increase. Note that the result does not depend on the outside pressure P0, the volume of the chamber V, or whether it is filled to P0.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


