
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Quantum Corrections to Equation of State
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 33
3-9-2016
1736
Quantum Corrections to Equation of State
Consider a noninteracting, one-component quantum gas at temperature τ, with a chemical potential μ in a cubic volume V. Treat the separate cases of bosons and fermions.
a) For a dilute system derive the equation of state in terms of temperature τ, pressure P, particle density n, and particle mass m. Do this derivation approximately by keeping the leading and next-leading powers of n. Interpret your results as an effective classical system.
b) At a given temperature, for which densities are your results valid?
SOLUTION
a) Start with the particle distribution over the absolute value of momentum:
 (1)
(1)
where the upper sign in (S.4.68.1) and below corresponds to Fermi statistics and the lower to Bose (g = 2s + 1). Using ε = p2/2m, we obtain
 (2)
(2)
The total energy is given by
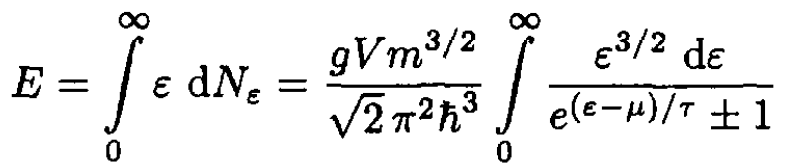 (3)
(3)
On the other hand, using the grand canonical potential Ω, where
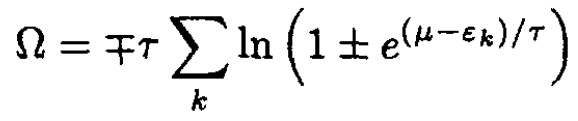 (4)
(4)
and replacing the sum by an integral, using (2), we obtain
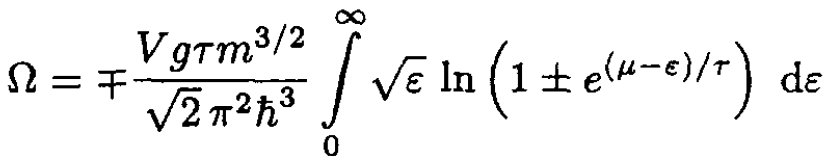 (5)
(5)
Integrating (5) by parts, we have
 (6)
(6)
Comparing this expression with (3), we find that
 (7)
(7)
However, Ω = F – μN = F – G = -PV. Therefore, we obtain the equation of state, which is valid both for Fermi and Bose gases (and is, of course, also true for a classical Boltzmann gas):
 (8)
(8)
Note that (8) was derived under the assumption of a particular dispersion law ε = p2/2m; for relativistic particles or photons with ε = pc, (8) becomes PV = E/3. From (8) and (3), we obtain
 (9)
(9)
where x ≡ ε/τ. (9) defines the equation of state. To find quantum corrections to the classical equation of state (which corresponds to the case eμ/τ << 1), expand the integral in (9), using exp (μ/τ – x) as a small parameter:
 (10)
(10)
Using Ω = -PV and substituting (10) into (9), we have
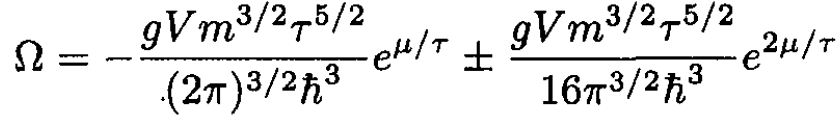 (11)
(11)
The first term, which we may call ΩB, corresponds to a Boltzmann gas with g = 1, and the second term gives the first correction
 (12)
(12)
Using the fact that, for small corrections
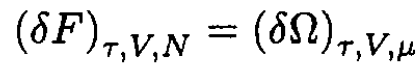
we can write the first quantum correction to the free energy F. Using the classical expression for μ in terms of τ and V gives the result to the same accuracy:
 (13)
(13)
Using

we obtain, from (13),
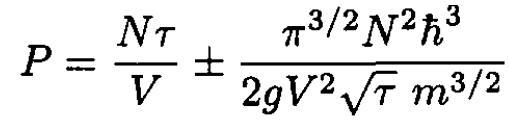 (14)
(14)
and
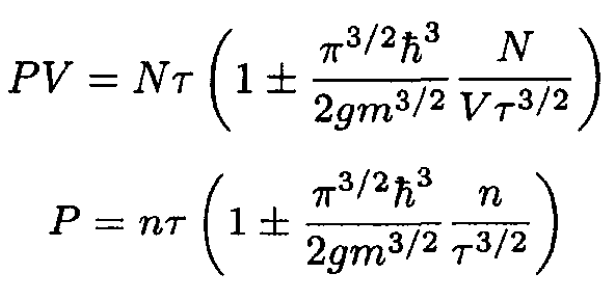 (15)
(15)
where n ≡ N/V.
b) The condition for validity of this approximation is that the first correction should be much less than unity:
 (16)
(16)
This gives the condition on the density for which (15) is valid:
 (17)
(17)
It is interesting to determine the de Broglie wavelength λdB at this temperature τ. We find that

We see that this approximation is valid when the separation between particles is much larger than the de Broglie wavelength. (16) expresses the same condition as for the applicability of Boltzmann statistics (which implies exp (μ/τ) << 1). Since the chemical potential μ may be written
 (18)
(18)
we see that
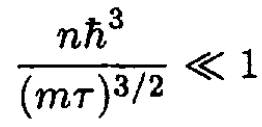
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















