
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Attractive Delta Function in 3D
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 78
14-8-2016
2163
Attractive Delta Function in 3D
A particle moves in three dimensions. The only potential is an attractive delta function at r = a of the form
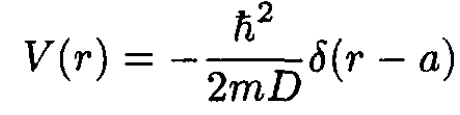 (i)
(i)
where D is a parameter which determines the strength of the potential.
a) What are the matching conditions at r = a for the wave function and its derivative?
b) For what values of D do bound states exist for s-wave (ℓ = 0).
SOLUTION
a) The amplitude of the wave function is continuous at the point r = a of the delta function. For the derivative we first note that the eigenfunctions are written in terms of a radial function R(r) and angular functions:
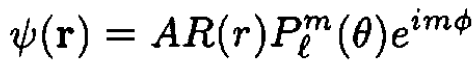 (1)
(1)
Since the delta function is only for the radial variable r, only the function R(r) has a discontinuous slope. From the radial part of the kinetic energy operator we integrate from r = a- to r = a+:
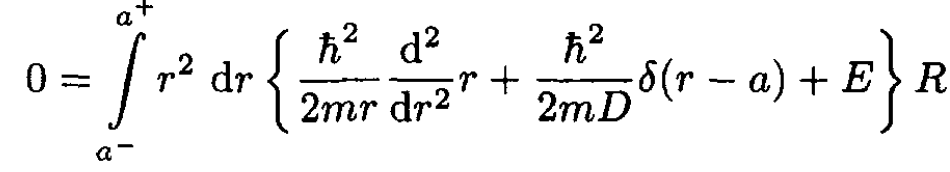 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
This formula is used to match the slopes at r = a.
b) In order to find bound states, we assume that the particle has an energy given by E = -h2α2/2m, where α needs to be determined by an eigenvalue equation. The eigenfunctions are combinations of exp (±α)/r. In order to be zero at r = 0 and to vanish at infinity, we must choose the form
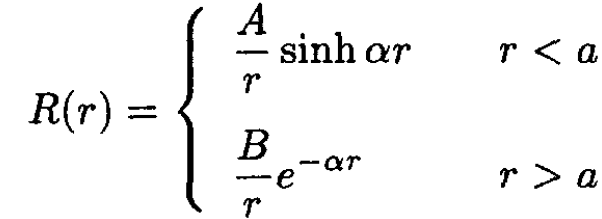 (4)
(4)
We match the values of R(r) at r = a. We match the derivative, using the results of part (a):
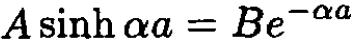 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
We eliminate the constants A and B and obtain the eigenvalue equation for α, which we proceed to simplify:
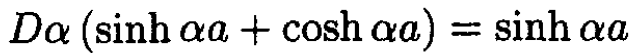 (7)
(7)
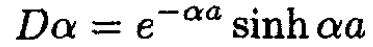 (8)
(8)
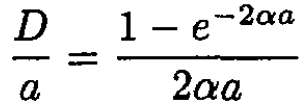 (9)
(9)
This is the eigenvalue equation which determines α as a function of parameters such as a, D, m etc. In order to find the range of allowed values of D for bound states, we examine αa → 0. The right-hand side of (9) goes to 1, which is its largest value. So, the constraint for the existence of bound states is
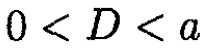 (10)
(10)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















