


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2024-04-09
Date: 2024-05-27
Date: 5-4-2022
|
Vowels and diphthongs TRAP, LOT, BATH, PALM
Southern BrC is a “broad-BATH” dialect like its input varieties. Short-O  and short-A
and short-A 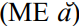 merged in the formation of JamC, as the latter never raised from [a] to [æ] according to Cassidy and LePage (1980: xlix), so pronunciations with [æ] represent StJamE or, more probably, BrE influence. Again targeting basilectal JamC as reference variety, BrC may dramatically reduce vowel-quality contrasts among low vowels (Patrick 1999). Though their ranges do not entirely overlap, all four word-classes share front, open variants, sometimes centralized (e.g. Sally); for some speakers TRAP and LOT may be merged, though others retain rounding on the latter. However, length distinctions are robust and may even be exaggerated relative to London English (Beckford Wassink [1999: 186] finds a 1.6:1 ratio for long-to-short in JamC, typical of languages where quantity is the primary distinction). Some Jamaican-born speakers alternate [a:] and [a:] in succession, both long.
merged in the formation of JamC, as the latter never raised from [a] to [æ] according to Cassidy and LePage (1980: xlix), so pronunciations with [æ] represent StJamE or, more probably, BrE influence. Again targeting basilectal JamC as reference variety, BrC may dramatically reduce vowel-quality contrasts among low vowels (Patrick 1999). Though their ranges do not entirely overlap, all four word-classes share front, open variants, sometimes centralized (e.g. Sally); for some speakers TRAP and LOT may be merged, though others retain rounding on the latter. However, length distinctions are robust and may even be exaggerated relative to London English (Beckford Wassink [1999: 186] finds a 1.6:1 ratio for long-to-short in JamC, typical of languages where quantity is the primary distinction). Some Jamaican-born speakers alternate [a:] and [a:] in succession, both long.
The possibly greater salience of quantity contrasts may account for the lengthening tendency observed in CLOTH words (normally short in South East England, Wells 1982) pronounced with front vowels; UK-born assimilated speakers tend to have short, backer vowels.
|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|