Hydration of Terminal Alkyne produces methyl ketones
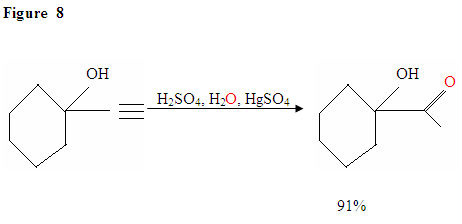
Just as described in Figure 7 the π electrons will attack a proton, forming a carbocation, which then gets attacked by the nucleophilic water molecules. After deprotination, we generate an enol, which then tautomerizes into the ketone form shown.
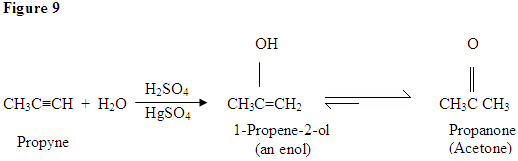
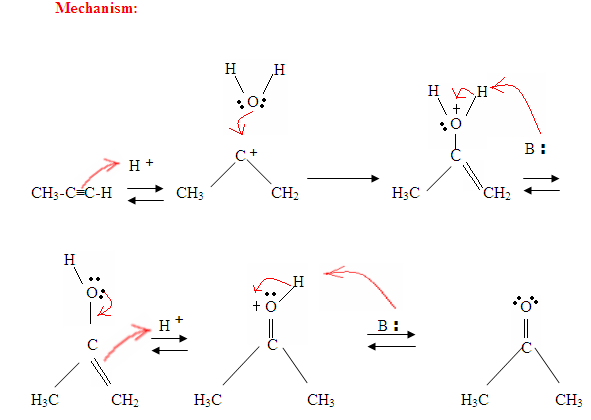
As you can see here, the π electrons of the triple bond are attacking the proton, which forms a covalent bond on the carbon with the most hydrogen substituents. Once the hydrogen is bound you have a carbocation, which gets attacked by the water molecule. Now you have a positive charge on the oxygen which results in a base coming in and deprotinating the molecule. Once deprotinated, you have an enol, which then gets tautomerized.
Tautomerism is shown here when the proton gets attacked by the double bond π electrons forming a covalent bond between the carbon and the hydrogen on the less substituted carbon. Electrons from the Oxygen end up moving to the carbon, forming a double bond with carbon and giving itself a positive charge, which then gets attacked by the base. The base deprotinates the Oxygen resulting in the more stable final product at equilibrium, which is a ketone.


