


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية| Steps in Translation : Translation regulation ,Protein folding and Protein targeting |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 30-11-2021
Date: 29-12-2021
Date: 7-12-2021
|
Steps in Translation : Translation regulation ,Protein folding and Protein targeting
Translation regulation
Gene expression is most commonly regulated at the transcriptional level, but translation may also be regulated. An important mechanism by whichthis is achieved in eukaryotes is by covalent modification of eIF-2: Phosphorylated eIF-2 is inactive . In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, regulation can also be achieved through proteins that bind mRNA and inhibit its use by blocking translation.
E. Protein folding
Proteins must fold to assume their functional, native state. Folding can be spontaneous (as a result of the primary structure) or facilitated by proteins known as chaperones .
F. Protein targeting
Although most protein synthesis in eukaryotes is initiated in the cytoplasm, many proteins perform their functions within subcellular organelles or outside of the cell. Such proteins normally contain amino acid sequences that direct the proteins to their final locations. For example, secreted proteins are targeted during synthesis (cotranslational targeting) to the RER by the presence of an N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence. The sequence is recognized by the signal recognition particle (SRP), a
ribonucleoprotein that binds the ribosome, halts elongation, and delivers the ribosome–peptide complex to an RER membrane channel (the translocon) via interaction with the SRP receptor. Translation resumes, the protein enters the RER lumen, and its signal sequence is cleaved (Fig. 1). The protein moves through the RER and the Golgi, is processed, packaged into vesicles, and secreted. Proteins targeted after synthesis (posttranslational) include nuclear proteins that contain an internal, short, basic nuclear localization signal; mitochondrial matrix proteins that contain an Nterminal, amphipathic, α-helical mitochondrial entry sequence; and peroxisomal proteins that contain a C-terminal tripeptide signal.
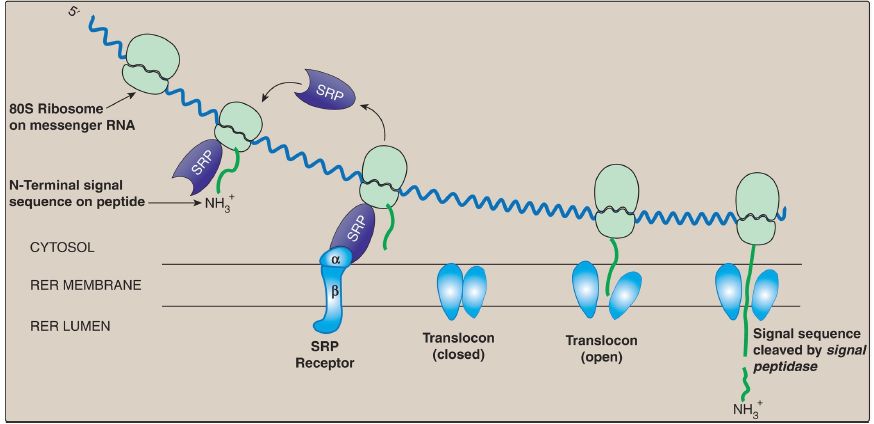
Figure 1: Cotranslational targeting of proteins to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). SRP = signal recognition particle.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|