


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 6-12-2021
Date: 1-11-2021
Date: 12-11-2021
|
Metabolic Map
Metabolism is best understood by examining its component pathways. Each pathway is composed of multienzyme sequences, and each enzyme, in turn, may exhibit important catalytic or regulatory features. A metabolic map containing the important central pathways of energy metabolism is presented in Figure 1.
This “big picture” view of metabolism is useful in tracing connections between pathways, visualizing the purposeful movement of metabolic intermediates (metabolites), and depicting the effect on the flow of intermediates if a pathway is blocked (for example, by a drug or an inherited deficiency of an enzyme). [Note: The metabolome is the full complement of metabolites in an organism.] Throughout the next three units of this book, each pathway under discussion will be repeatedly featured as part of the major metabolic map shown in Figure1.
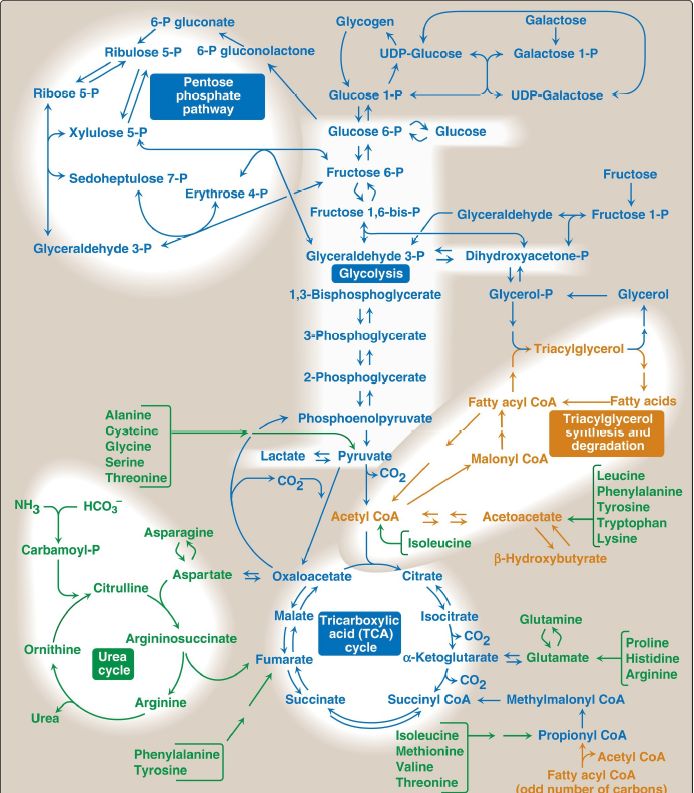
Figure 1: Important reactions of intermediary metabolism. Several important pathways to be discussed in later chapters are highlighted. Curved reaction arrows () indicate forward and reverse reactions that are catalyzed by different enzymes. The straight arrows () indicate forward and reverse reactions that are catalyzed by the same enzyme. Blue text = intermediates of carbohydrate metabolism; brown text = intermediates of lipid metabolism; green text = intermediates of protein metabolism. UDP = uridine diphosphate; P = phosphate; CoA = coenzyme A; CO2 = carbon dioxide; HCO3 - = bicarbonate; NH3 =ammonia.



|
|
|
|
كل ما تود معرفته عن أهم فيتامين لسلامة الدماغ والأعصاب
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ماذا سيحصل للأرض إذا تغير شكل نواتها؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر العدد 112 من مجلة حيدرة للفتيان
|
|
|