
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Molar Specific Heat of Helium Gas
المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
المصدر:
Physics 2000
الجزء والصفحة:
490
9-12-2020
2532
Molar Specific Heat of Helium Gas
A gas of helium atoms is about the simplest substance you can picture. Since helium does not form molecules, the gas simply consists of individual atoms moving around and bouncing off of each other. If the temperature of the gas is T, then the average thermal kinetic energy of the atoms is 3/2 kT.
If you have a mole of helium gas at a temperature T, then the thermal energy of the atoms should be the average energy of 1 atom, 3/2 kT, times the number NA atoms in a mole. Thus we easily estimate that the thermal energy EHe of a mole of helium atoms is

Using the fact that NAk = R, the gas constant, we get
If we raise the temperature one degree, from T to (T + 1), the thermal energy goes from 3/2 RT to 3/2 R(T + 1), an increase of 3/2 R. Thus the molar specific heat, which we will call CV , is
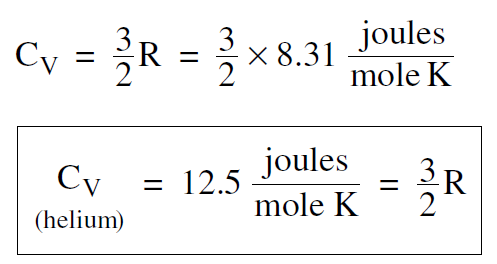 ......(1)
......(1)
As we mentioned, we get the right answer. Equation 1 is in agreement with experiment.
The subscript V on the symbol CV is there to remind us to measure the specific heat at constant volume. If you add heat to a gas, and at the same time allow the gas to expand, some of the energy goes into the work required to expand the volume, pushing the surrounding gas aside. For now we will leave the subscript V on CV to remind us not to let the volume increase.
 الاكثر قراءة في الديناميكا الحرارية
الاكثر قراءة في الديناميكا الحرارية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















