


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 15-9-2020
Date: 11-3-2021
Date: 15-12-2016
|
Tangential Distance, Velocity and Acceleration
So far we have used the model of a rotating shaft to illustrate the concepts of angular distance, velocity and acceleration. We now wish to shift the focus of our discussion to the dynamics of a particle traveling along a circular path. For this we will use the model of a small mass m on the end of a massless stick of length r shown in Figure (1). The other end of the stick is attached to and is free to rotate about a fixed axis at the origin of our coordinate system. The presence of the stick ensures that the mass m travels only along a circular path of radius r. The quantity θ( t ) is the angular distance travelled and ω( t ) the angular velocity of the particle.
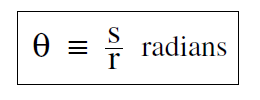 .......(i)
.......(i)
When we are discussing the motion of a particle in a circular orbit, we often want to know how far the particle has travelled, or how fast it is moving. The distance s along the path (we could call the tangential distance) travelled is given by Equation (i) as
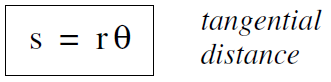 ........(1)
........(1)

Figure 1: Mass rotating on the end of a massless stick.
The speed of the particle along the path, which we can call the tangential speed vt, is the time derivative of the tangential distance s(t)
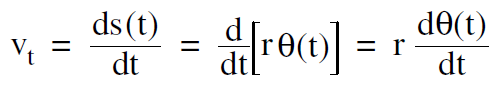
where r comes outside the derivative since it is constant. Since dθ (t) /dt is the angular velocity ω, we get
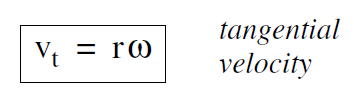
The tangential acceleration at , the acceleration of the particle along its path, is the time derivative of the tangential velocity
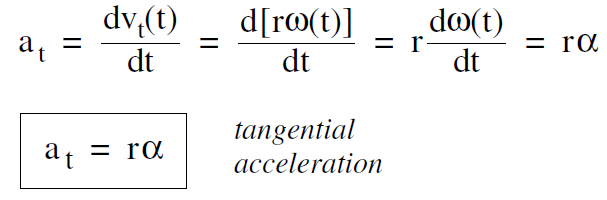
where again we took the constant r outside the derivative, and used α = dω/dt .



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تسليم.. مجلة أكاديمية رائدة في علوم اللغة العربية وآدابها
|
|
|