


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 28-4-2020
Date: 2-5-2020
Date: 2-5-2020
|
The underlying order of a crystalline solid can be represented by an array of regularly spaced points that indicate the locations of the crystal's basic structural units. This array is called a crystal lattice. Crystal lattices can be thought of as being built up from repeating units containing just a few atoms. These repeating units act much as a rubber stamp: press it on the paper, move ("translate") it by an amount equal to the lattice spacing, and stamp the paper again.
|
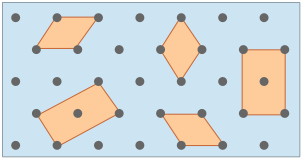
The gray circles represent a square array of lattice points. |
The orange square is the simplest unit cell that can be used to define the 2-dimensional lattice. |
Building out the lattice by moving ("translating") the unit cell in a series of steps, |
Although real crystals do not actually grow in this manner, this process is conceptually important because it allows us to classify a lattice type in terms of the simple repeating unit that is used to "build" it. We call this shape the unit cell. Any number of primitive shapes can be used to define the unit cell of a given crystal lattice. The one that is actually used is largely a matter of convenience, and it may contain a lattice point in its center, as you see in two of the unit cells shown here. In general, the best unit cell is the simplest one that is capable of building out the lattice.

Shown above are unit cells for the close-packed square and hexagonal lattices we discussed near the start of this lesson. Although we could use a hexagon for the second of these lattices, the rhombus is preferred because it is simpler.
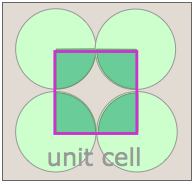
Notice that in both of these lattices, the corners of the unit cells are centered on a lattice point. This means that an atom or molecule located on this point in a real crystal lattice is shared with its neighboring cells. As is shown more clearly here for a two-dimensional square-packed lattice, a single unit cell can claim "ownership" of only one-quarter of each molecule, and thus "contains" 4 × ¼ = 1 molecule.
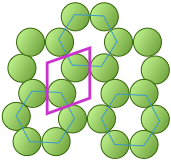
The unit cell of the graphite form of carbon is also a rhombus, in keeping with the hexagonal symmetry of this arrangement. Notice that to generate this structure from the unit cell, we need to shift the cell in both the x- and y- directions in order to leave empty spaces at the correct spots. We could alternatively use regular hexagons as the unit cells, but the x+y shifts would still be required, so the simpler rhombus is usually preferred. As you will see in the next section, the empty spaces within these unit cells play an important role when we move from two- to three-dimensional lattices.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|