


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 3-12-2015
Date: 23-9-2019
Date: 3-12-2015
|
The aldol reaction is potentially a powerful synthetic tool. As demonstrated by the following equation, a directed aldol reaction between different aldehydes would produce a single crossed aldol product (the new bond is colored maroon) and create two new stereogenic centers (colored blue). However, conducting this reaction with aqueous NaOH usually generates a mixture of four different adducts, and frequently β-elimination of water when possible.
R1CH2CHO |
+ |
R2CH2CHO |
base |
R1CH2CH(OH)—CH(R2)CHO |
| Carbonyl Acceptor | Enolate Donor | One Crossed Aldol Product |
In this section methods of controlling the enolate donor and carbonyl acceptor reactants to produce a single aldol product will be described and discussed. Several important principles must be taken into consideration for this purpose.
• The conventional aldol reaction is reversible. (aqueous base at room temperature)
• The initial aldol product may undergo beta-elimination of water, depending on reaction conditions.
• Regioselective enolate anion formation may be achieved by using differences in kinetic vs. equilibrium acidities of α-hydrogens.
• Enolate anions may be trapped as silyl ethers and used subsequently for controlled aldol reactions.
• Enolate-like species may be used for aldol-like reactions with carbonyl compounds, and hydrolyzed later to aldol products.
• Metal cations or other electrophilic moieties may act to orient the reactants in specific ways.
The reversibility of conventional aldol reactions is illustrated by the crossed aldol condensation of 2-butanone with benzaldehyde, illustrated below. The methyl hydrogens are kinetically more acidic than the methylene hydrogens, so the α'-enolate is generated more rapidly than the more substituted α-enolate. As a rule, ketone enolate bases react more rapidly with aldehydes than with ketones, so self condensation of the ketone is minimal. Both enolate anions add reversibly to benzaldehyde to form β-hydroxy ketones; however, the α-enolate product (on the left) reverts to reactants faster than it eliminates water. In contrast, the isomeric α'-enolate product (on the right) undergoes rapid β-elimination to the observed 5-phenyl-4-penten-3-one final product.
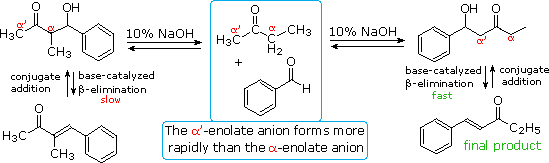
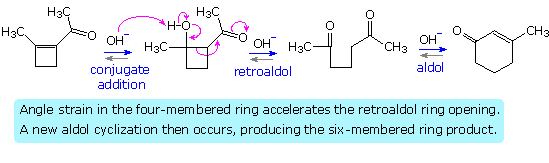
Acid catalysis of the 2-butanone-benzaldehyde reaction gives the isomer, 3-methyl-4-phenyl-3-buten-2-one, as the chief product, thanks to the predominance of the more substituted α-enol as an intermediate. In this case both β-hydroxy ketone intermediates undergo reversible dehydration.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|