

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Natural classes
المؤلف:
April Mc Mahon
المصدر:
An introduction of English phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
46-4
17-3-2022
3974
Natural classes
The major class features identify several categories of sounds which recur cross-linguistically in different phonological rules. Feature notation can also show why certain sounds behave similarly in similar contexts, within these larger classes. For instance, English /p/, /t/ and /k/ aspirate at the beginnings of words. All three may also be glottally reinforced at the ends of words. All three are unaspirated after /s/; and no other English phoneme has the same range of allophones, in the same environments. In feature terms, although /p/, /t/, /k/ differ in place of articulation, all three are obstruent consonants, and within this class, are [– voice, – nasal, – continuant]. A group of phonemes which show the same behavior in the same contexts, and which share the same features, constitute a natural class. More formally, a natural class of phonemes can be identified using a smaller number of features than any individual member of that class. As (12) shows, the class of voiceless plosives, /p/, /t/ and /k/, can be defined uniquely using only three features. If we subtract one of the plosives, we need more features, since we must then specify the place of articulation; and the same is true in defining a single plosive unambiguously.

Phonological rules very typically affect natural classes of phonemes. For example, medial voicing of /f/ to [v] in Old English, did not only affect that labial fricative, but also the other members of the voiceless fricative class, /s/ and /θ/. If we wrote a rule for /f/ alone, it would have to exclude the other voiceless fricatives, so that the input would have to include [+anterior, – coronal]; however, the more general fricative voicing rule in (13) requires fewer features to characterize the input, as we would expect when a natural class is involved.
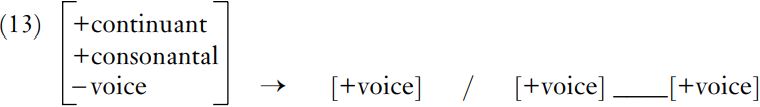
This rule also neatly captures the connection between the process and its conditioning context, and therefore shows the motivation for the development: the fricatives, which are generally voiceless, becomes voiced between voiced sounds. This will often mean between vowels, as in heofon and hlaford; but it may also mean between a vowel and a voiced consonant, as in hæfde. If voicing takes place between voiced sounds, instead of having to switch off vocal fold vibration for a single segment and then switch it back on again, the vocal folds can continue vibrating through the whole sequence. Voicing the fricative in this context is therefore another example of assimilation, where one sound is influenced by another close to it in the utterance.
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















