


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 21-11-2019
Date: 25-5-2017
Date: 28-10-2020
|
Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alkenes: Allylic Bromination
We’ve already seen several methods for preparing alkyl halides from alkenes, including the reactions of HX and X2 with alkenes in electrophilic addition reactions. The hydrogen halides HCl, HBr, and HI react with alkenes by a polar mechanism to give the product of Markovnikov addition. Bromine and chlorine undergo anti addition through halonium ion intermediates to give 1,2-dihalogenated products.

Another laboratory method for preparing alkyl halides from alkenes is by reaction with N-bromosuccinimide (abbreviated NBS), in the presence of light, to give products resulting from substitution of hydrogen by bromine at the position next to the double bond—the allylic position. Cyclohexene, for example, gives 3-bromocyclohexene.
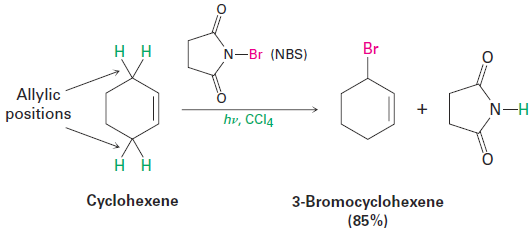
This allylic bromination with NBS is analogous to the alkane chlorination reaction discussed in the previous section and occurs by a radical chainreaction pathway (Figure 1.1). As in alkane halogenation, a Br· radicala bstracts an allylic hydrogen atom, forming an allylic radical plus HBr. The HBr then reacts with NBS to form Br2, which in turn reacts with the allylic radical to yield the brominated product and a Br· radical that cycles back into the first step and carries on the chain.
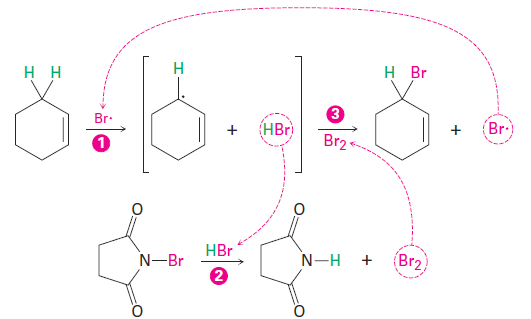
Figure 1.1 Mechanism of allylic bromination of an alkene with NBS. The process is a radical chain reaction in which ( 1 ) a Br· radical abstracts an allylic hydrogen atom of the alkene and gives an allylic radical plus HBr. ( 2 ) The HBr then reacts with NBS to form Br2, which ( 3 ) reacts with the allylic radical to yield the bromoalkene product and a Br· radical that continues the chain.
Why does bromination with NBS occur exclusively at an allylic position rather than elsewhere in the molecule? The answer, once again, is found by looking at bond dissociation energies to see the relative stabilities of various kinds of radicals. Although a typical secondary alkyl C - H bond has a strength of about 410 kJ/mol (98 kcal/mol) and a typical vinylic C -H bond has a strength of 465 kJ/mol (111 kcal/mol), an allylic C - H bond has a strength of only about 370 kJ/mol (88 kcal/mol). An allylic radical is therefore more stable than a typical alkyl radical with the same substitution by about 40 kJ/mol (9 kcal/mol).




|
|
|
|
مخاطر خفية لمكون شائع في مشروبات الطاقة والمكملات الغذائية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"آبل" تشغّل نظامها الجديد للذكاء الاصطناعي على أجهزتها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تستخدم لأول مرة... مستشفى الإمام زين العابدين (ع) التابع للعتبة الحسينية يعتمد تقنيات حديثة في تثبيت الكسور المعقدة
|
|
|