


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 3-10-2016
Date: 6-10-2016
Date: 5-10-2016
|
EXAMPLE 1: DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO SETS. As a first and simple example, let

for A = S1, the unit sphere in R2: a ∈ S1 if and only if |a|2 = a21 +a22 = 1. In other words, we are considering only curves that move with unit speed.
We take
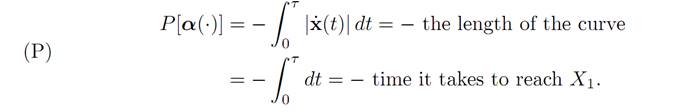
We want to minimize the length of the curve and, as a check on our general theory, will prove that the minimum is of course a straight line.
Using the maximum principle. We have
H(x, p, a) = f (x, a) p + r(x, a)
= a . p − 1 = p1a1 + p2a2 − 1.
The adjoint dynamics equation (ADJ) says
p˙ (t) = −∇xH(x(t), p(t),α(t)) = 0,
and therefore
p(t) ≡ constant = p0= 0.
The maximization principle (M) tells us that
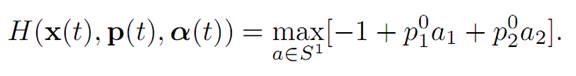
The right hand side is maximized by

a unit vector that points in the same
direction of p0. Thus α(.) ≡ a0 is constant in time. According then to (ODE) we have x˙ = a0, and consequently x(.) is a straight line.
Finally, the transversality conditions say that
(T) p(0) ⊥ T0, p(t1) ⊥ T1.
In other words, p0 ⊥ T0 and p0 ⊥ T1; and this means that the tangent planes T0 and T1 are parallel.

Now all of this is pretty obvious from the picture, but it is reassuring that the general theory predicts the proper answer.
EXAMPLE 2: COMMODITY TRADING. Next is a simple model for the trading of a commodity, say wheat. We let T be the fixed length of trading period, and introduce the variables
x1 (t) = money on hand at time t
x2 (t) = amount of wheat owned at time t
α(t) = rate of buying or selling of wheat
q(t) = price of wheat at time t (known)
λ = cost of storing a unit amount of wheat for a unit of time.
We suppose that the price of wheat q(t) is known for the entire trading period 0 ≤ t ≤ T (although this is probably unrealistic in practice). We assume also that the rate of selling and buying is constrained:
|α(t)| ≤ M,
where α(t) > 0 means buying wheat, and α(t) < 0 means selling.
Our intention is to maximize our holdings at the end time T, namely the sum of the cash on hand and the value of the wheat we then own:
(P) P[α(.)] = x1 (T) + q(T)x2 (T).
The evolution is
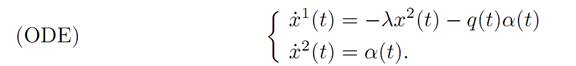
This is a nonautonomous (= time dependent) case, but it turns out that the Pontryagin Maximum Principle still applies.
Using the maximum principle. What is our optimal buying and selling strategy? First, we compute the Hamiltonian
H(x, p, t, a) = f. p + r = p1(−λx2 − q(t)a) + p2a,
since r ≡ 0. The adjoint dynamics read

with the terminal condition
(T) p(T) = ∇g(x(T)).
In our case g(x1, x2) = x1 + q(T)x2, and hence

We then can solve for the costate:
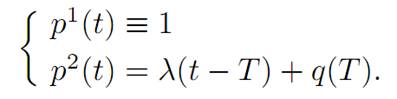
The maximization principle (M) tells us that
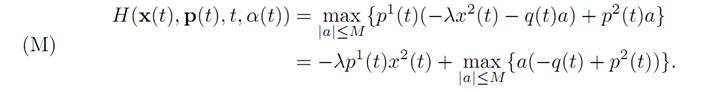

CRITIQUE. In some situations the amount of money on hand x1(.) becomes negative for part of the time. The economic problem has a natural constraint x2 ≥ 0 (unless we can borrow with no interest charges) which we did not take into account in the mathematical model.
References
[B-CD] M. Bardi and I. Capuzzo-Dolcetta, Optimal Control and Viscosity Solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equations, Birkhauser, 1997.
[B-J] N. Barron and R. Jensen, The Pontryagin maximum principle from dynamic programming and viscosity solutions to first-order partial differential equations, Transactions AMS 298 (1986), 635–641.
[C1] F. Clarke, Optimization and Nonsmooth Analysis, Wiley-Interscience, 1983.
[C2] F. Clarke, Methods of Dynamic and Nonsmooth Optimization, CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics, SIAM, 1989.
[Cr] B. D. Craven, Control and Optimization, Chapman & Hall, 1995.
[E] L. C. Evans, An Introduction to Stochastic Differential Equations, lecture notes avail-able at http://math.berkeley.edu/˜ evans/SDE.course.pdf.
[F-R] W. Fleming and R. Rishel, Deterministic and Stochastic Optimal Control, Springer, 1975.
[F-S] W. Fleming and M. Soner, Controlled Markov Processes and Viscosity Solutions, Springer, 1993.
[H] L. Hocking, Optimal Control: An Introduction to the Theory with Applications, OxfordUniversity Press, 1991.
[I] R. Isaacs, Differential Games: A mathematical theory with applications to warfare and pursuit, control and optimization, Wiley, 1965 (reprinted by Dover in 1999).
[K] G. Knowles, An Introduction to Applied Optimal Control, Academic Press, 1981.
[Kr] N. V. Krylov, Controlled Diffusion Processes, Springer, 1980.
[L-M] E. B. Lee and L. Markus, Foundations of Optimal Control Theory, Wiley, 1967.
[L] J. Lewin, Differential Games: Theory and methods for solving game problems with singular surfaces, Springer, 1994.
[M-S] J. Macki and A. Strauss, Introduction to Optimal Control Theory, Springer, 1982.
[O] B. K. Oksendal, Stochastic Differential Equations: An Introduction with Applications, 4th ed., Springer, 1995.
[O-W] G. Oster and E. O. Wilson, Caste and Ecology in Social Insects, Princeton UniversityPress.
[P-B-G-M] L. S. Pontryagin, V. G. Boltyanski, R. S. Gamkrelidze and E. F. Mishchenko, The Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes, Interscience, 1962.
[T] William J. Terrell, Some fundamental control theory I: Controllability, observability, and duality, American Math Monthly 106 (1999), 705–719.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|