


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 9-8-2016
Date: 13-7-2016
Date: 8-8-2016
|
Isothermal Compression and Adiabatic Expansion of Ideal Gas
An ideal gas is compressed at constant temperature τ from volume V1 to volume V2 (see Figure 1.1).
a) Find the work done on the gas and the heat absorbed by the gas.
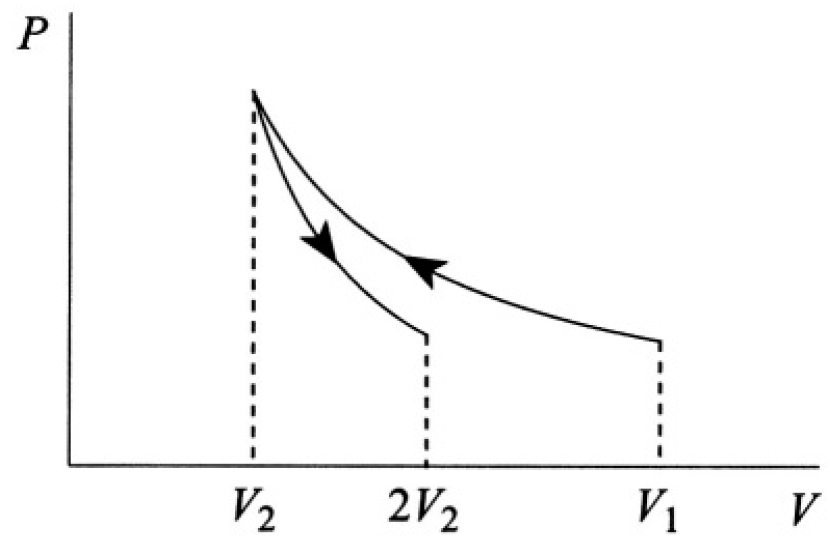
Figure 1.1
b) The gas now expands adiabatically to volume 2V2. What is the final temperature Tf (derive this result from first principles)?
c) Estimate Tf for Ti = 300 K for air.
SOLUTION
We can a) calculate the work as an integral, using the ideal gas law:
 (1)
(1)
where τ is, as usual, the absolute temperature. Graphically, it is simply the area under the curve (see Figure 1.2). Alternatively, we can say that the work done is equal to the change of free energy F of the system:
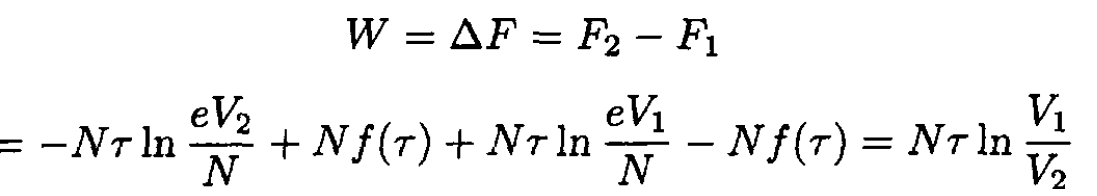 (2)
(2)

Figure 1.2
The total energy ε of the ideal gas depends only on the temperature, which is constant, so the heat absorbed by the gas is
 (3)
(3)
i.e., heat is rejected from the gas into the reservoir. Alternatively, since δQ = τ dS,
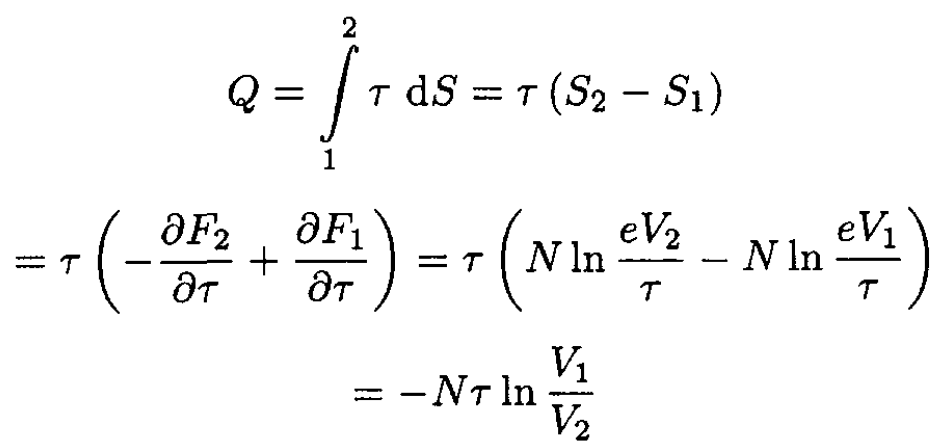 (4)
(4)
the same result as in (3).
b) For an adiabatic expansion the entropy is conserved, so
 (5)
(5)
On the other hand,
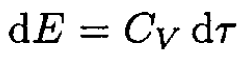 (6)
(6)
where CV is the specific heat for an ideal gas at constant volume. From (5) and (6), and using the ideal gas law, we obtain
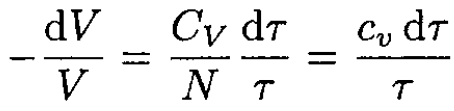 (7)
(7)
where CV/N ≡ cv, the specific heat per one molecule. Integrating (7) yields
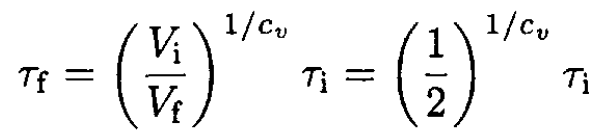 (8)
(8)
c) For air we may take cv = 5/2 (in regular units, cv = 5kB/2, it is mostly diatomic). Therefore,




|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|