


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 27-2-2021
Date: 26-4-2016
Date: 10-12-2015
|
Glutamine (Gln, Q(
The amino acid glutamine is incorporated into the nascent polypeptide chain during protein biosynthesis in response to two codons—CAA and CAG—and represents approximately 4.0% of the residues of the proteins that have been characterized. The glutaminyl residue incorporated has a mass of 128.14 Da, a van der Waals volume of 114 Å 3, and an accessible surface area of 189 Å2. Gln residues have close to average conservation during divergent evolution; they are interchanged in homologous proteins most frequently with Glutamic Acid (Glu, E)and Histidine (His, H) residues.
The side chain of Gln residues is the same as that of glutamic acid, except that the carboxyl group has been converted to the amide:

Both amino acids occur naturally and are incorporated directly into proteins during their biosynthesis. Gln residues do not arise from amidation of Glu in proteins. The amide side chain does not ionize and is not very reactive chemically. It is polar, however, as it is both a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor. The amide group is labile at extremes of pH and at high temperatures, and Gln residues can deamidate to Glu, although usually less rapidly than Asn residues do.
When Gln residues are at the N-terminus of a peptide chain, they spontaneously cyclize:
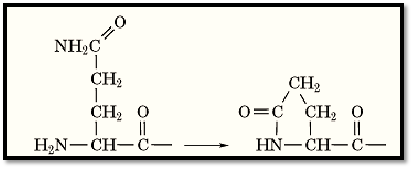
The resulting residue of pyrrolidone carboxylic acid renders the N-terminus unreactive in most procedures for sequencing proteins, such as the Edman Degradation. This residue can be removed, however, by the enzyme pyroglutamyl amino peptidase .



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|