


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 16-2-2017
Date: 16-2-2017
Date: 16-3-2016
|
Determination of plasma glucose
Choice of blood specimen:
Because of the large number of determinations on individual diabetic patients, capillary blood has often been used. Plasma glucose is higher than the concentration in whole blood. This may be corrected by multiplying the whole blood glucose concentrations by 1.15 and adding 0.33 mmol/L to derive the plasma or serum glucose.
Plasma is preferred to serum as the blood can be added directly to the mixture of anticoagulant and preservative and then separated immediately. This gives a larger sample for analysis than serum from the same volume of blood and there is less glycolysis. If serum is used it must be separated as soon as possible, but not later than 30 to 40 min after blood collection.
Glucose Oxidase Methods
In these methods, the aldehyde group of β–D-glucose is oxidized by glucose oxidase to give gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide.

Reagents:
1. Preparation of protein precipitant:
Dissolve 10 g sodium tungstate (Na2WO4,2H2O)
+ 9 g sodium chloride
+10 g disodium hydrogen phosphate
in about 800 ml water.
Add about 125 ml 1.0 M hydrochloric acid to bring the pH to 3 using narrow range indicator paper.
Add 1g phenol and make to 1 liter with water.
2. Preparation of color reagent:
Mix 75 ml disodium hydrogen phosphate solution (40g Na2HPO4 /L)
+ 215 ml water
+ 5ml peroxidase
+ 300 mg sodium azide
+ 100 mg 4-aminophenazone.
3. Preparation of standard glucose solution:
10 mM (1.8 g/l) in benzoic acid (10 g/L).
Technique:
Calculation:
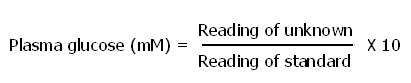



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|