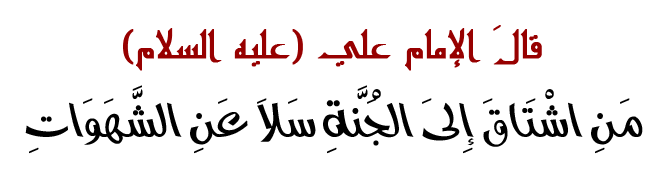
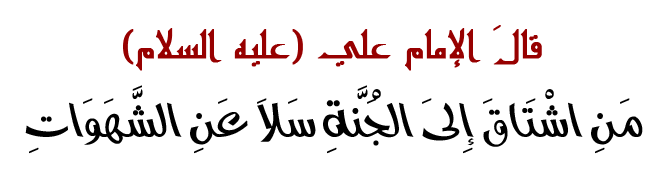

 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2024-04-10
Date: 14-3-2022
Date: 2024-07-05
|
As is normal in many language varieties, vowels in JamC are nasalized in the environment of nasal consonants. The examples below demonstrate this.

There is a phonological rule which applies to monosyllabic grammatical morphemes ending in a nasal consonant. This vowel may be deleted leaving only the nasalization on the vowel to signal its underlying presence. Note that, in the case of /wan/, which has both a lexical meaning ‘one’, and that of the indefinite article, it is only the latter, as shown in (5) a. below, which allows for the optional deletion of the final nasal.

Distinct from nasal allophones of the vowel phonemes, there is a nasal vowel phoneme. This vowel is /ãã/ with the phonetic realization of [ã:]. It appears in a small number of quite regularly used words. In the examples below, we see a case of a contrast in identical environments, involving the first pair, and, in the second pair, a contrast in analogous environments. These contrasts establish the phonemic status of /ãã/ in relation the phonetically closest vowel phoneme, /aa/, independent of suprasegmental features, which remain constant in each member of the pairs below.

JamC syllables with /ãã/ as their nucleus tend to have an equivalent syllable in JamE cognates consisting of the vowel /aa/ or /çç/ and a post-vocalic /nt/ cluster. Even though /nt/ exists in the vast majority of JamC items with English /nt/ cognates, e.g. /plaant/ ‘plant’, /aant/ ‘haunt’, etc., a small group of items such as /wãã/ ‘want’ and /kjãã/ ‘can’t’ appear in JamC minus the word final /nt/ cluster of the English cognate. It is this fact which creates the lexical contrast.
|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|