


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 15-7-2021
Date: 16-7-2021
Date: 2025-01-19
|
Neck Fascia
The neck is surrounded by a protective layer of subcutaneous adipose that makes up the superficial cervical fascia. It is further divided into multiple compartments by layers of deep cervical fascia.
A. Superficial cervical fascia
Cutaneous nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels and nodes can be found within the fatty substance of the superficial cervical fascia. The platysma muscle-a muscle of facial expression running from the inferior mandible to infraclavicular fascia-is also located in this layer.
B. Deep cervical fascia
The deep cervical fascia is a series of connective tissue cylinders arranged into four main layers-the investing, visceral (pretrachealand buccopharyngeal), prevertebral, and carotid sheath/alar fascia layers (Fig. 1).
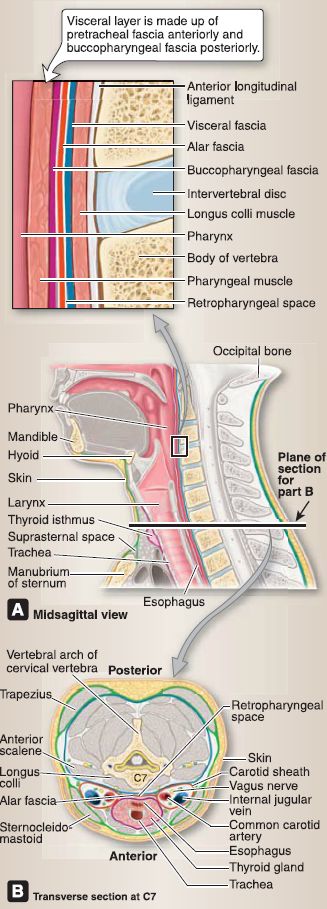
Figure 1: Fascial layers and spaces in the neck. A, Note structures forming retropharyngeal space. B, Compartments and fascial arrangement. Superficial cervical fascia: yellow = subcutaneous tissue of neck. Layers of deep cervical fascia: Green = investing layer, Violet = visceral layer, Blue = prevertebral layer, Red = alar fascia and carotid sheath.
1. Investing layer: The tough investing layer encompasses the structures of the neck in a single connective tissue sheet. It splits to completely enclose the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscles and forms sheaths around the parotid and submandibular glands.
2. Visceral layer: This layer is subdivided into anterior pretracheal and posterior buccopharyngeal layers. It encompasses neck viscera, including the thyroid gland, trachea, esophagus (pretracheal), and the pharyngeal constrictor and buccinators muscles (buccopharyngeal).
3. Prevertebral layer: This layer encloses the vertebrae and associated neck musculature.
4. Carotid sheath and alar fascia: The carotid sheath is a tubal structure that extends from the base of the skull to the root of the neck and contains the common and internal carotid arteries, internal jugular vein, vagus nerve, lymph nodes, sympathetic fibers, and the nerve to the carotid sinus. The alar fascia extends between right and left carotid sheaths within the retropharyngeal space.
C. Retropharyngeal space
The retropharyngeal space is the largest space between fascial layers in the neck. It is found anterior to the prevertebral fascia and posterior to the buccopharyngeal fascia. The space functions to allow movement of the neck viscera on the vertebral column during swallowing but can also be a conduit for the spread of infection, inflammation, and air into the thorax (see Fig. 1A).



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أصواتٌ قرآنية واعدة .. أكثر من 80 برعماً يشارك في المحفل القرآني الرمضاني بالصحن الحيدري الشريف
|
|
|