


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 7-4-2021
Date: 24-4-2021
Date: 9-4-2021
|
Parts of a power supply
A power supply provides the proper voltage and current for electronic apparatus. Most power supplies consist of several stages, always in the same order (Fig. 1).
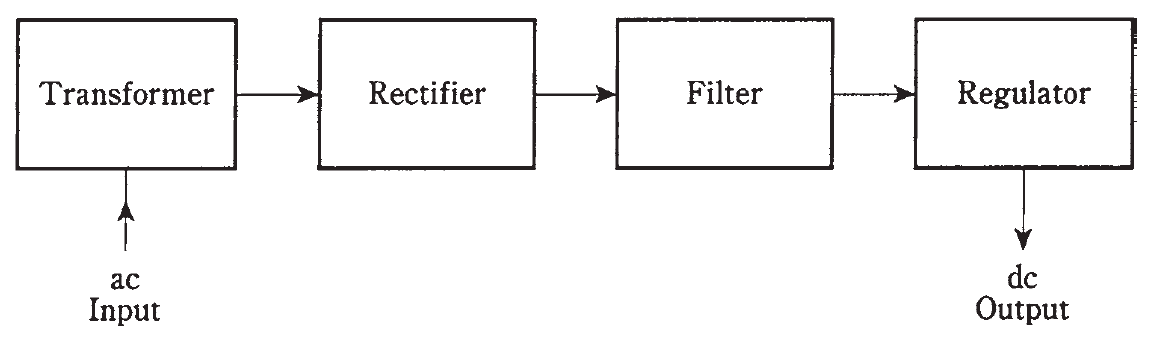
Fig. 1: Block diagram of a power supply. Sometimes a regulator is not needed.
First, the ac encounters a transformer that steps the voltage either down or up, depending on the exact needs of the electronic circuits. Second, the ac is rectified, so that it becomes pulsating dc with a frequency of either 60 Hz or 120 Hz. This is almost always done by one or more semiconductor diodes.
Third, the pulsating dc is filtered, or smoothed out, so that it becomes a continuous voltage having either positive or negative polarity with respect to ground.
Finally, the dc voltage might need to be regulated. Some equipment is finicky, insisting on just the right amount of voltage all the time. Other devices can put up with some voltage changes.
Power supplies that provide more than a few volts must have features that protect the user (that’s you!) from receiving a dangerous electrical shock. All power supplies need fuses and/or circuit breakers to minimize the fire hazard in case the equipment shorts out.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|