
THE BEGINNING OF QUANTUM MECHANICAL VIEW
 المؤلف:
Shabnam Siddiqui
المؤلف:
Shabnam Siddiqui
 المصدر:
Quantum Mechanics
المصدر:
Quantum Mechanics
 الجزء والصفحة:
9
الجزء والصفحة:
9
 21-3-2021
21-3-2021
 1944
1944
THE BEGINNING OF QUANTUM MECHANICAL VIEW
The pioneering work of Planck led to the new law of radiation known as Planck’s radiation law. This new law can be summarized as following:
Planck’s radiation law: The sources of thermal radiation are atoms in a state of oscillations, and vibrational energy of each oscillator may have any of a series of discrete values but never any value in between. The energy E an oscillating atom can have is given as:
En = n h ν ...........(1)
where n = 1, 2, 3,…, h = Planck’s constant, and ν = the frequency of the oscillator. When an oscillator (oscillating atom) changes from a higher state of energy E2 to a state of lower energy E1, it emits discrete amount of energy as E2 − E1 = h ν. This smallest amount of energy is called as quanta of energy. When an oscillator changes its energy state from lower (E1) to a higher energy state (E2), it absorbs a quantum of energy. Planck illustrated the mechanism of emission and absorption of radiation and the fact that it is only the energy of the radiation that is quantized. He still considered the radiation to be an electromagnetic wave.
Later, this idea was further advanced by Einstein, who suggested that light, which is an electromagnetic wave, is made up of discrete elementary particles called photons. The energy carried by a photon is a function of its frequency: Ephoton = hν. We will discuss this in more details in the next section. The schematic that follows describes the change in views of radiation after the discovery of Planck (Figure 1).
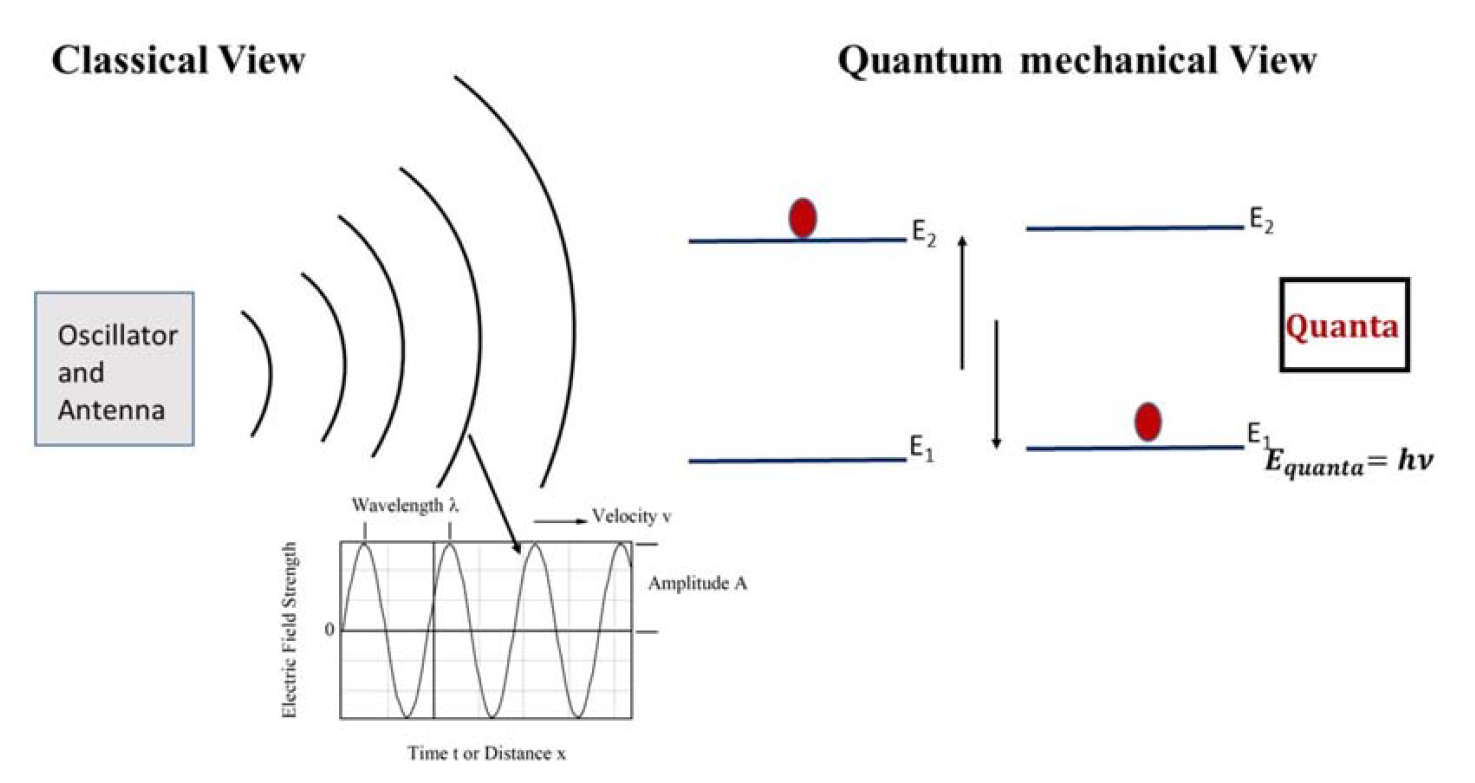
FIGURE 1: A schematic showing the differences in the classical and quantum mechanical view of radiation. According to classical electromagnetism, an oscillating charged particle, such as electron oscillating with some frequency, emits an electromagnetic wave of the same frequency continuously, moving with the speed of light in a vacuum, whereas according to Planck, an oscillating charged particle emits radiation discontinuously. It emits radiation only when it transitions from a higher energy state to a lower energy state. The frequency of the radiation it emits depends on the energy difference between the higher and lower energy levels.
 الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


