
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Circular apertures and angular resolving power
المؤلف:
George C. King
المصدر:
Vibrations and Waves
الجزء والصفحة:
177
7-2-2021
2585
Circular apertures and angular resolving power
A circular aperture will also produce a diffraction pattern. This pattern will, of course, have circular symmetry. For a plane wave that falls normally on a small circular aperture, the diffraction pattern appears as a central bright disc surrounded by a series of bright and dark rings. This central disc is called the Airy disc in honour of Sir George Airy, a former Astronomer Royal of England, and contains 84% of the integrated light intensity. The dark rings correspond to the zeros of intensity in the diffraction pattern. For an aperture of diameter d, the first zeros on either side of the central maximum occur at angles ±θR, where
 ..........(1)
..........(1)
 ......(i)
......(i)
This equation has the same form as Equation (i) but with the multiplying factor 1.22. The angular diameter of the central bright disc is equal to the angular distance between these two zeros on either side of the central maximum, i.e. 2.44λ/d. Consequently, when a lens or mirror images a point-like object such as a distant star, it does not produce a point-like image even when lens aberrations can be discounted. Instead the light is spread out into a diffraction pattern. This has important practical consequences for image formation by lenses and mirrors since it limits their ability to resolve closely spaced objects, like two stars that are close together in our field of view. We are able to just resolve their images if the maximum of the diffraction pattern from one object falls at the first minimum of the pattern from the other, accordingly to the Rayleigh criterion. This is illustrated in Figure 1, which shows the two diffraction patterns arising from two point objects. The dotted line is the sum of the two diffraction patterns and illustrates that we can just distinguish the two diffraction maxima. It follows that we would just be able to distinguish the two point images. The angular separation of two objects is the same as the angular separation of their images. Hence, two point objects are just resolvable by a lens or mirror of diameter d when their angular separation θ satisfies
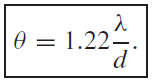

Figure 1: Two overlapping diffraction patterns at the image plane of a lens or mirror, arising from two point objects. The dotted line is the sum of the two diffraction patterns. The Rayleigh criterion states that the images of the two point objects can be just resolved when the maximum of one diffraction pattern overlaps the first minimum of the other. This is the case shown.
If two objects with a spatial separation b are at a large distance L from a lens or mirror, then we can write θ = b/L. Hence we can just resolve them if b = 1.22λL/d. For example, if we assume a size of 3 mm for a human pupil and an optical wavelength of 550 nm, we have
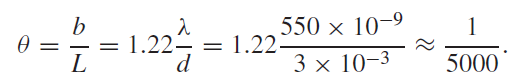
This suggests that we can read a car number plate at a distance of ∼100 m, assuming that we need to resolve features ∼2 cm apart. In radio astronomy the wavelengths of interest are much longer than for visible light. For example, atomic hydrogen produces what is known as 21 centimetre radiation and this is used extensively in radio astronomy. The diameter of the Lovell telescope at Jodrell Bank, UK, is 76 m. At the wavelength of 21 cm, it has an angular resolution ∼1/300 for which θ ∼ 0.2◦. Similar considerations apply to microscopy. In an electron microscope the wavelengths associated with the electrons may be 100,000 times shorter than for visible light and so sharp images of extremely small objects can be obtained. Diffraction also limits the amount of information that can be stored on optical recording media like compact discs. There is no point in making the dimensions of the pattern printed on the disc smaller than the diffraction limit of the optical imaging system that is used to read it.
 الاكثر قراءة في الفيزياء العامة
الاكثر قراءة في الفيزياء العامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















