


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 20-3-2016
Date: 23-1-2021
Date: 9-11-2020
|
Michelson spectral interferometer
Young’s double-slit experiment is an example of interference by division of wavefront, where we take two portions of the wavefront to obtain the two coherent wave sources. We can also have interference by division of amplitude where the primary wave itself is divided into two parts by, for example, a semi-silvered mirror. An important example of division of amplitude is the Michelson spectral interferometer. This interferometer provided one of the key experimental observations underpinning the theory of relativity. It is also a powerful research tool with many applications including the determination of the emission spectra of atoms and molecules, i.e. the wavelengths of their emitted radiations. In particular, it can do this with very high spectral resolution. The principle of operation of the Michelson spectral interferometer is illustrated in Figure 1. A beam of light from
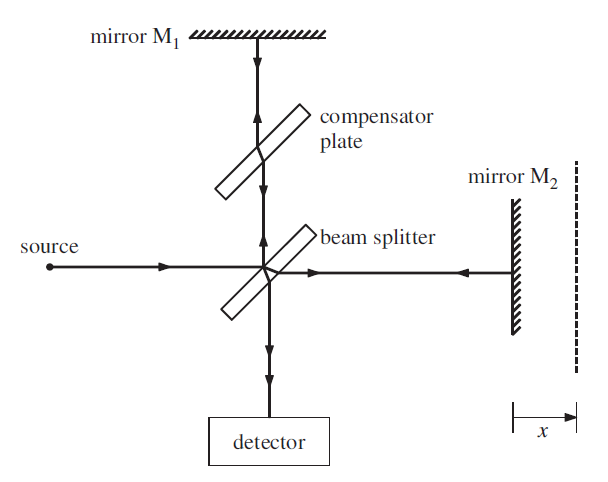
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the Michelson spectral interferometer.
a monochromatic source is split into two equal beams by the semi-reflecting front face of the beam splitter . The two separate beams travel to mirrors M1 and M2, respectively, and then return to the beamsplitter from where they travel along the same path to the detector. The presence of the compensator plate ensures that the beams transverse the same total thickness of glass in both arms of the interferometer. The two superposed beams have the same intensity at the detector since each undergoes one transmission and one reflection at the semi-reflecting surface of the beamsplitter. Mirror M1 is fixed in position. The position of mirror M2 can be adjusted with a very fine micrometer screw. If the path lengths of the two beams are the same or are different by an integral number of wavelengths, the beams will interfere constructively at the detector and there will be a maximum in the detected light intensity. However, if the path lengths are different by an odd number of half-wavelengths, there will be destructive interference and the detected light intensity will be zero. When the detected light intensity is plotted as a function of the displacement x of mirror M2 an interference pattern is obtained, as shown in Figure 2. The separation of adjacent interference maxima is equal to λ/2 where λ is the wavelength and hence the value of λ may be determined.
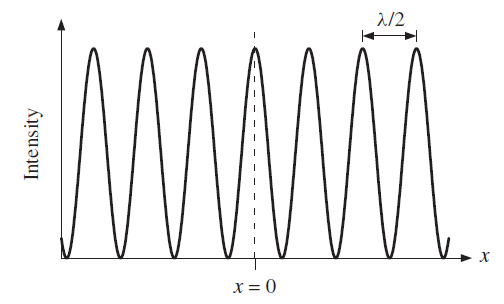
Figure 2 The interference pattern observed with a Michelson spectral interferometer. The measured light intensity is plotted as a function of the displacement x of the moveable mirror M2. The separation of the maxima in the measured intensity is equal to λ/2, where λ is the wavelength of the light.



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مشاتل الكفيل تزيّن مجمّع أبي الفضل العبّاس (عليه السلام) بالورد استعدادًا لحفل التخرج المركزي
|
|
|