


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 3-3-2016
Date: 3-3-2016
Date: 22-8-2020
|
The constant of aberration
The constant of aberration is officially defined as being equal to the ratio of the speed of a planet of negligible mass, moving in a circular orbit of unit radius, to the velocity of light. It is expressed in seconds of arc by multiplying this ratio by the number of seconds of arc in 1 radian. A value of 20''·496 is now adopted.
If we consider the Earth’s orbit as circular, the Earth’s distance from the Sun, a, to be 149 600 × 106 m, the number of seconds in 1 sidereal year, T, to be 31·56 × 106 and the velocity of light, c, to be 299 792·5 × 103 m s−1, we have
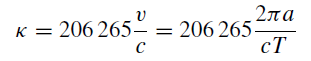
giving
κ = 20''·492.
In fact, the Earth’s orbit has eccentricity e = 0·016 74 and the more correct expression for κ is
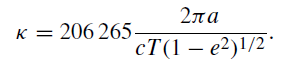 ............(1)
............(1)
we may write
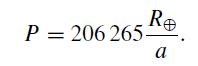 ..........(2)
..........(2)
where P is the solar parallax (measured in seconds of arc) and R⊕ is the Earth’s radius. By equations (1) and (2), we have
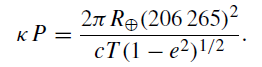 ..........(4)
..........(4)
The quantities on the right-hand side of this expression being known accurately, it was formerly thought that the accurate measurement of κ would enable an accurate value to be obtained for the solar parallax and hence of the scale of the Solar System. Unfortunately the measurement of κ, by means of meridian circle observations in which the observed declinations of stars were found, is tied in with a phenomenon called the variation of latitude. The Earth’s crust shifts slightly with respect to the Earth’s axis of rotation so that the latitude of an observatory is not quite fixed. Modern methods of measuring the solar parallax and the value of the astronomical unit by radar are much more accurate and so the expression is best used to determine a value of κ from a knowledge of P.
In The Astronomical Almanac and other almanacs, tables are provided enabling the observer to allow for the effects of aberration on the right ascension and declination of the stars. Quantities C and D, depending upon the Sun’s longitude, are given for every day of the year. Then if (α, δ) and (α1, δ1) are the equatorial coordinates of the positions of the star unaffected and affected by aberration,
α1 − α = Cc + Dd
δ1 − δ = Cc' + Dd'
where c, d, c', d' are functions of the star’s coordinates.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|