
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
The angle of aberration
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
الجزء والصفحة:
p 136
3-8-2020
1983
The angle of aberration
Bradley remembered this work of Roemer, neglected for half a century. He also knew that the velocity of the Earth in its heliocentric orbit was about 30 km s−1 in a direction always at right angles to it radius vector (assuming the Earth’s orbit to be circular). He now had all the information required to explain the phenomena he had observed and produce a formula to predict them.
In everyday life we are familiar with a number of examples embodying the principle involved. For instance, in a stationary car on a rainy day we see the raindrops stream downwards. But when the car moves, the raindrops’ paths slant so that they appear to be coming from a direction between directly overhead and the direction in which the car is travelling.

Figure 1. The effect of aberration.
In figure 1, let light from a star X enter a telescope at A so that the observer sees the star in the middle of the field of view. The telescope, because of the Earth’s orbital velocity v km s−1, is moving in the direction EE1. By the time the light travelling with velocity c km s−1 (c = 299 792·5 km s−1) has reached the foot of the telescope, the telescope has moved into the position E1B. To the observer, the star appears to lie in the direction E1B because the telescope has had to be tilted slightly away from the true direction of the star towards the instantaneous direction in which the observer is moving.
The angle of aberration, Δθ, is obtained by considering ΔAEE1 in which the distances EE1 and AE1 are proportional to v and c respectively. If we take ∠AE1D = θ and ∠AED = θ1, then


Figure 2. The aberrational ellipse.
or

Hence,
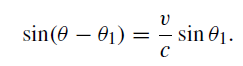
Remembering that θ − θ1 = Δθ is a small angle (the quantity v/c ∼ 1/10 000), and expressing Δθ in seconds of arc, we may write

or
Δθ = κ sin θ. (1)
The constant κ is called the constant of aberration; its value is 20''·496. The angle of aberration
Δθ obviously depends upon the value of θ, the angle between the star’s direction and the instantaneous direction in which the observing is travelling. This is the direction D in which the Earth is moving, a direction known as the apex of the Earth’s way (figure 2) and which has a longitude always 90◦ less than that of the Sun ( DS). The Sun possessed that longitude three months previously, which Bradley realized was the explanation why his observations were always three months out of step with the ones he expected. Just as in the case of stellar parallax, the star appears to move in an ellipse about its heliocentric position X and just as in the case of parallax, it may easily be shown that the major axis of this ellipse, of value 40''·992, is parallel to the ecliptic. The shape of this aberrational ellipse obviously depends upon the star’s position on the celestial sphere. For a star on the ecliptic, the ellipse degenerates into an arc of length 2κ and for a star at the pole of the ecliptic, the ellipse is a circle.
DS). The Sun possessed that longitude three months previously, which Bradley realized was the explanation why his observations were always three months out of step with the ones he expected. Just as in the case of stellar parallax, the star appears to move in an ellipse about its heliocentric position X and just as in the case of parallax, it may easily be shown that the major axis of this ellipse, of value 40''·992, is parallel to the ecliptic. The shape of this aberrational ellipse obviously depends upon the star’s position on the celestial sphere. For a star on the ecliptic, the ellipse degenerates into an arc of length 2κ and for a star at the pole of the ecliptic, the ellipse is a circle.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















