


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 14-12-2020
Date: 2-9-2019
Date: 27-11-2019
|
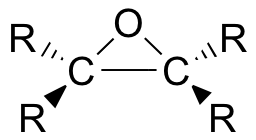
Epoxides (also known as oxiranes) are three-membered ring structures in which one of the vertices is an oxygen and the other two are carbons.
The most important and simplest epoxide is ethylene oxide which is prepared on an industrial scale by catalytic oxidation of ethylene by air.
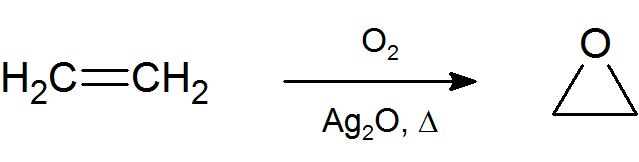
Ethylene oxide is used as an important chemical feedstock in the manufacturing of ethylene glycol, which is used as antifreeze, liquid coolant and solvent. In turn, ethylene glycol is used in the production of polyester and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) the raw material for plastic bottles.
Oxacyclopropane synthesis by peroxycarboxylic acid requires an alkene and a peroxycarboxylic acid as well as an appropriate solvent. The peroxycarboxylic acid has the unique property of having an electropositive oxygen atom on the COOH group. The reaction is initiated by the electrophilic oxygen atom reacting with the nucleophilic carbon-carbon double bond. The mechanism involves a concerted reaction with a four-part, circular transition state. The result is that the originally electropositive oxygen atom ends up in the oxacyclopropane ring and the COOH group becomes COH.
.png?revision=1)
Epoxides can also be synthesized by the treatment of a halohydrin with a base. This causes an intramolecular Williamson ether synthesis.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|