


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 11-10-2020
Date: 26-11-2019
Date: 7-9-2018
|
A second model for a nucleophilic substitution reaction is called the 'dissociative', or 'SN1' mechanism: in this picture, the C-X bond breaks first, before the nucleophile approaches:
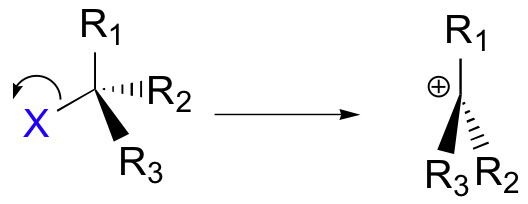
This results in the formation of a carbocation: because the central carbon has only three bonds, it bears a formal charge of +1. Recall that a carbocation should be pictured as sp2 hybridized, with trigonal planar geometry. Perpendicular to the plane formed by the three sp2 hybrid orbitals is an empty, unhybridized p orbital.

In the second step of this two-step reaction, the nucleophile attacks the empty, 'electron hungry' p orbital of the carbocation to form a new bond and return the carbon to tetrahedral geometry.
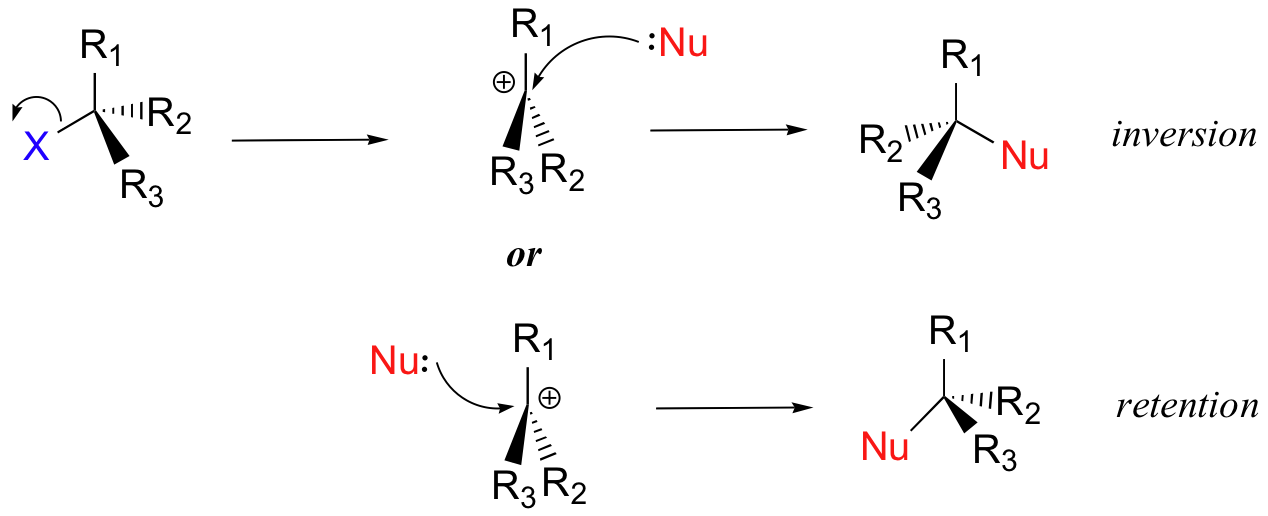
We saw that SN2 reactions result specifically in inversion of stereochemistry at the electrophilic carbon center. What about the stereochemical outcome of SN1 reactions? In the model SN1 reaction shown above, the leaving group dissociates completely from the vicinity of the reaction before the nucleophile begins its attack. Because the leaving group is no longer in the picture, the nucleophile is free to attack from either side of the planar, sp2-hybridized carbocation electrophile. This means that about half the time the product has the same stereochemical configuration as the starting material (retention of configuration), and about half the time the stereochemistry has been inverted. In other words, racemization has occurred at the carbon center. As an example, the tertiary alkyl bromide below would be expected to form a racemic mix of R and S alcohols after an SN1 reaction with water as the incoming nucleophile.

Exercise 1.1
Draw the structure of the intermediate in the two-step nucleophilic substitution reaction above.
The SN1 reaction we see an example of a reaction intermediate, a very important concept in the study of organic reaction mechanisms that was introduced earlier in the module on organic reactivity Recall that many important organic reactions do not occur in a single step; rather, they are the sum of two or more discreet bond-forming / bond-breaking steps, and involve transient intermediate species that go on to react very quickly. In the SN1 reaction, the carbocation species is a reaction intermediate. A potential energy diagram for an SN1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of valley in the path of the reaction, higher in energy than both the reactant and product but lower in energy than the two transition states.
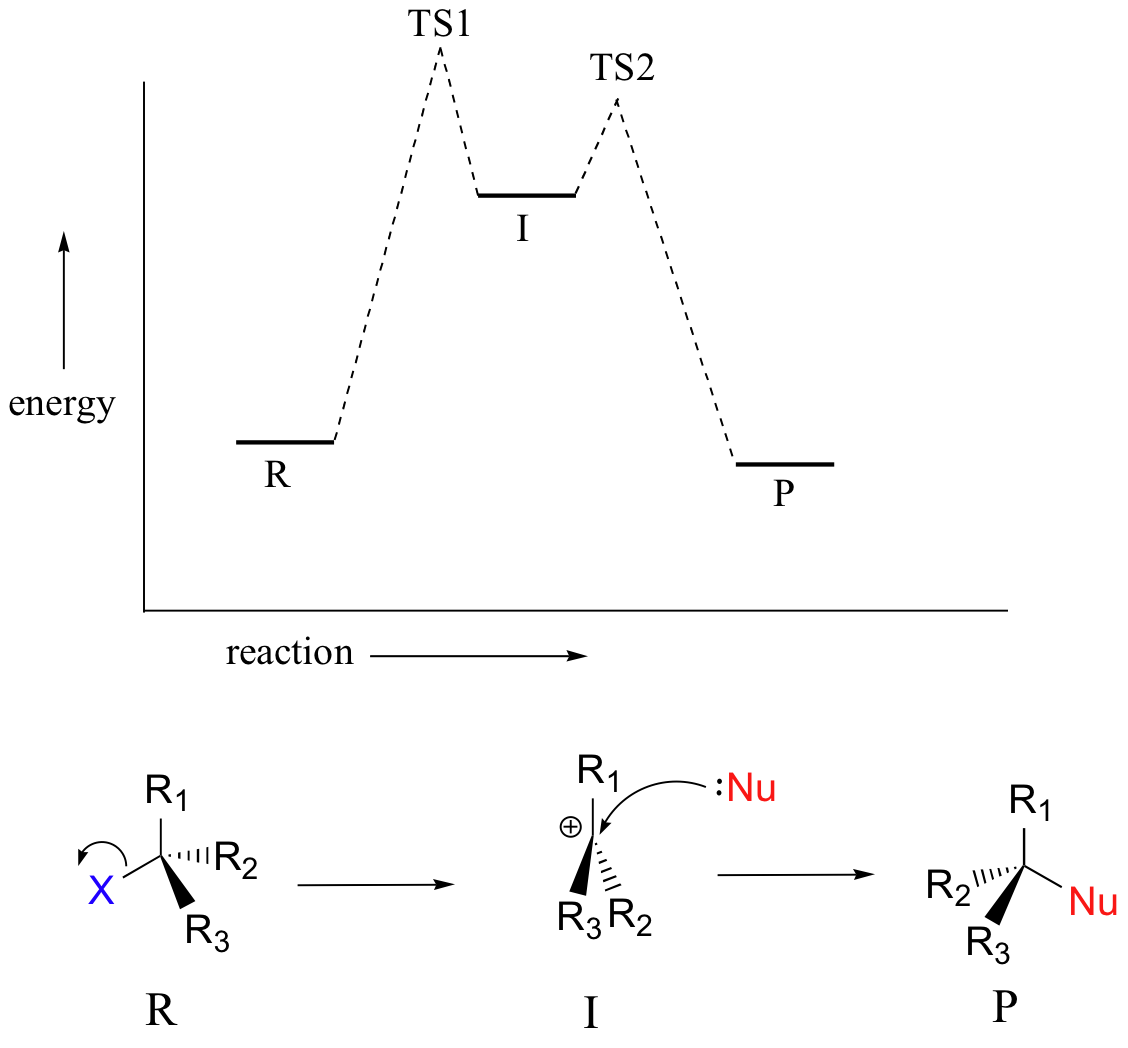



|
|
|
|
من بينها تفادي حب الشباب.. فوائد مذهلة للاستحمام في المساء
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بمناسبة مرور 40 يومًا على رحيله الهيأة العليا لإحياء التراث تعقد ندوة ثقافية لاستذكار العلامة المحقق السيد محمد رضا الجلالي
|
|
|