


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 6-7-2019
Date: 31-12-2019
Date: 23-5-2017
|
Addition reactions of isolated dienes proceed more or less as expected from the behavior of simple alkenes. Thus, if one molar equivalent of 1,5-hexadiene is treated with one equivalent of bromine a mixture of 5,6-dibromo-1-hexene, 1,2,5,6-tetrabromohexane and unreacted diene is obtained, with the dibromo compound being the major product (about 50%).
CH2=CH(CH2)2CH=CH2 + Br2  |
BrCH2CHBr(CH2)2CH=CH2 + | BrCH2CHBr(CH2)2CHBrCH2Br + | CH2=CH(CH2)2CH=CH2 |
| 5,6-dibromo-1-hexene | 1,2,5,6-tetrabromohexane | 1,5-hexadiene |
Similar reactions of conjugated dienes, on the other hand, often give unexpected products. The addition of bromine to 1,3-butadiene is an example. As shown below, a roughly 50:50 mixture of 3,4-dibromo-1-butene (the expected product) and 1,4-dibromo-2-butene (chiefly the E-isomer) is obtained. The latter compound is remarkable in that the remaining double bond is found in a location where there was no double bond in the reactant. This interesting relocation requires an explanation.
CH2=CH-CH=CH2 + Br2  |
BrCH2CHBr-CH=CH2 + | BrCH2CH=CHCH2Br |
| 3,4-dibromo-1-butene | 1,4-dibromo-2-butene |
The expected addition product from reactions of this kind is the result of 1,2-addition, i.e. bonding to the adjacent carbons of a double bond. The unexpected product comes from 1,4-addition, i.e. bonding at the terminal carbon atoms of a conjugated diene with a shift of the remaining double bond to the 2,3-location. These numbers refer to the four carbons of the conjugated diene and are not IUPAC nomenclature numbers. Product compositions are often temperature dependent, as the addition of HBr to 1,3-butadiene demonstrates.
CH2=CH-CH=CH2 + HBr  reaction temperature |
CH3CHBr-CH=CH2 + 1,2 addition yield |
CH3CH=CHCH2Br 1,4 addition yield |
| 0 ºC 40 ºC |
70% 15% |
30% 85% |
Bonding of an electrophilic atom or group to one of the end carbon atoms of a conjugated diene (#1) generates an allyl cation intermediate. Such cations are stabilized by charge delocalization, and it is this delocalization that accounts for the 1,4-addition product produced in such addition reactions. As shown in the diagram, the positive charge is distributed over carbons #2 and #4 so it is at these sites that the nucleophilic component bonds. Note that resonance stabilization of the allyl cation is greater than comparable stabilization of 1,3-butadiene, because charge is delocalized in the former, but created and separated in the latter.
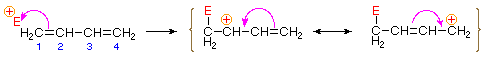
An explanation for the temperature influence is shown in the following energy diagram for the addition of HBr to 1,3-butadiene. The initial step in which a proton bonds to carbon #1 is the rate determining step, as indicated by the large activation energy (light gray arrow). The second faster step is the product determining step, and there are two reaction paths (colored blue for 1,2-addition and magenta for 1,4-addition). The 1,2-addition has a smaller activation energy than 1,4-addition, but the 1,4-product is more stable than the 1,2-product. At low temperatures, the products are formed irreversibly and reflect the relative rates of the two competing reactions. This is termed kinetic control. At higher temperatures, equilibrium is established between the products, and the thermodynamically favored 1,4-product dominates.
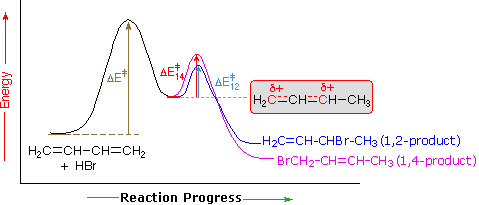



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة توجه دعوة لجامعة القادسية للمشاركة في حفل التخرج المركزي
|
|
|