

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
English plosives
المؤلف:
Peter Roach
المصدر:
English Phonetics and Phonology A practical course
الجزء والصفحة:
37-4
2024-10-13
1520
English plosives
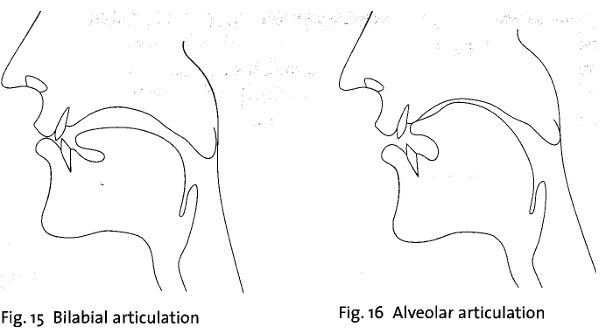
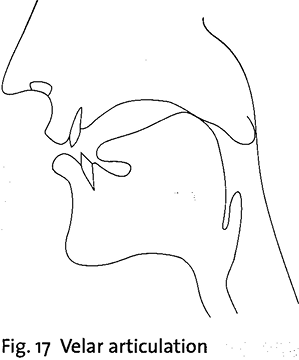
English has six plosive consonants: p, t, k, b, d, g. The glottal plosive ? occurs frequently but it is of less importance, since it is usually just an alternative pronunciation of p, t, k in certain contexts. The plosives have different places of articulation. The plosives p, b are bilabial since the lips are pressed together (Fig. 15); t, d are alveolar since the tongue blade is pressed against the alveolar ridge (Fig. 16). Normally the tongue does not touch the front teeth as it does in the dental plosives found in many languages. The plosives k, g are velar; the back of the tongue is pressed against the area where the hard palate ends and the soft palate begins (Fig. 17).
The plosives p, t, k are always voiceless; b, d, g are sometimes fully voiced, sometimes partly voiced and sometimes voiceless. We will consider what b, d, g should be called later.
All six plosives can occur at the beginning of a word (initial position), between other sounds (medial position) and at the end of a word (final position). To begin with we will look at plosives preceding vowels (which can be abbreviated as CV, where C stands for a consonant and V stands for a vowel), between vowels (VCV) and following vowels (VC). We will look at more complex environments later.
i) Initial position (CV): The closing phase for p, t, k and b, d, g takes place silently. During the compression phase there is no voicing in p, t, k; in b, d, g there is normally very little voicing - it begins only just before the release. If the speaker pronounces an initial b, d, g very slowly and carefully there may be voicing during the entire compression phase (the plosive is then fully voiced), while in rapid speech there may be no voicing at all.
The release of p, t, k is followed by audible plosion - that is, a burst of noise. There is then, in the post-release phase, a period during which air escapes through the vocal folds, making a sound like h. This is called aspiration. Then the vocal folds come together and voicing begins. The release of b, d, g is followed by weak plosion, and this happens at about the same time as, or shortly after, the beginning of voicing. The most noticeable and important difference, then, between initial p, t, k and b, d, g is the aspiration of the voiceless plosives p, t, k. The different phases of the plosive all happen very rapidly, but the ear distinguishes clearly between p, t, k and b, d, g. If English speakers hear a fully voiced initial plosive, they will hear it as one of b, d, g but will notice that it does not sound quite natural.
If they hear a voiceless unaspirated plosive they will also hear that as one of b, d, g, because it is aspiration, not voicing which distinguishes initial p, t, k from b, d, g. Only when they hear a voiceless aspirated plosive will they hear it as one of p, t, k; experiments have shown that we perceive aspiration when there is a delay between the sound of plosion and the beginning (or onset) of voicing.
In initial position, b, d, g cannot be preceded by any consonant, but p, t, k may be preceded by s. When one of p, t, k is preceded by s it is unaspirated. From what was said above it should be clear that the unaspirated p, t, k of the initial combinations sp, st, sk have the sound quality that makes English speakers perceive a plosive as one of b, d, g; if a recording of a word beginning with one of sp, st, sk is heard with the s removed, an initial b, d or g is perceived by English speakers.
• Medial position (VCV): The pronunciation of p, t, k and b, d, g in medial position depends to some extent on whether the syllables preceding and following the plosive are stressed. In general we can say that a medial plosive may have the characteristics either of final or of initial plosives
• Final position (VC): Final b, d, g normally have little voicing; if there is voicing, it is at the beginning of the compression phase; p, t, k are always voiceless. The plosion following the release of p, t, k and b, d, g is very weak and often not audible. The difference between p, t, k and b, d, g is primarily the fact that vowels preceding p, t, k are much shorter. The shortening effect of p, t, k is most noticeable when the vowel is one of the long vowels or diphthongs. This effect is sometimes known as pre-fortis clipping.
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonetics and Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonetics and Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















