


 9:35:24
9:35:24  2019-03-07
2019-03-07  1176
1176
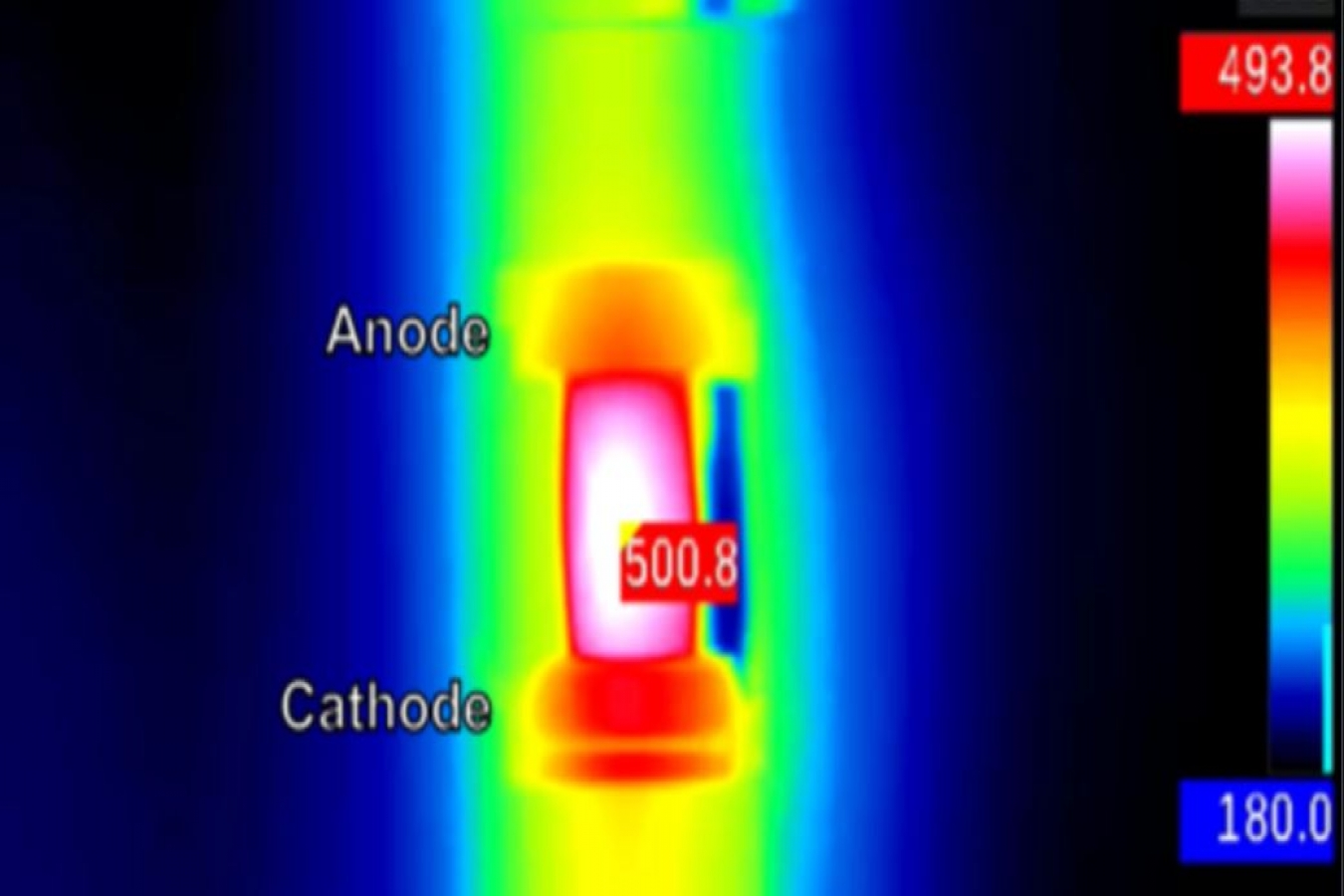
The glass shouldn't have boiled. But it did.
A team of physicists zapped small cubes of glass in a furnace with an electric voltage about what you'd get from an outlet in your home. It was enough electricity to heat up the glass, which was already quite warm from the ambient heat of the furnace. But it shouldn't have been enough current to boil the glass. Glass doesn't boil until it reaches temperatures thousands of degrees above what the current should have produced. And yet, in their oven, when the current flowed and created an electric field, the physicists saw a thin "wisp of vapor" rising from the glass sample.
For that to happen, the electric current would have had to concentrate in one part of the glass, delivering its energy unevenly. But there's a problem: That's against the law.
Here's the deal: When an electric current passes through a uniform material, it's supposed to heat the whole material evenly. Scientists call this Joule's first law, after the British chemist James Prescott Joule, who discovered it in the early 1840s. It's a material fact with roots in the law of conservation of energy, one of the most fundamental rules that govern our universe. And we see it at work every day; light-bulb filaments wouldn't have their nice, even glow without Joule's law at work.
But this current seemed to break the law. Not only did vapor rise from some parts of the glass, but a hotspot (visible on an infrared camera) danced giddily across its surface. Again and again in their experiments, hotspots appeared.
"This glass is uniform on the most minute level," Himanshu Jain, a materials scientist at Lehigh University in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, and co-author of a paper describing the phenomenon published Feb. 26 in the journal Nature Scientific Reports.
Glass is an insulator and doesn't carry current well; however small, it is expected to turn most of that current into heat. Conventional thinking about Joule's first law would predict that an electric current would heat the glass evenly, causing it to slowly melt and deform, Jain told Live Science. And under most circumstances, that's exactly what happens.
"We looked at the softening of hot glass under an electric field," Jain said, "and that's the thing that nobody had done before."
That uneven heating, it turned out, was dumping loads of energy near the anode in the glass, the entry point for the current. So the glass was melting and evaporating there, even as it stayed solid elsewhere. The temperatures in the hotspots were much hotter than the rest of the glass. At one point, a single region of the glass heated by about 2,500 F (1,400 C) in less than 30 seconds.
So was Joule's law broken? Yes and no, Jain said; macroscopically thinking, it appeared so. Microscopically speaking, the answer would be "no" — it just didn't apply to the glass as a whole anymore.
Under Joule's first law, a uniform electric field should heat a material evenly. But at high temperatures, the electric field doesn't only heat the glass — it changes its chemical makeup.
Electric fields move through glass when positively charged ions (atoms stripped of negatively charged electrons) get knocked out of position and carry a charge across the glass, Jain said. The lightest ions move first, carrying the electrical current.
The glass in this setup was made of oxygen, sodium and silicon. Sodium, the loosely-bonded lightweight ion, did most of the energy transport. Once enough sodium shifted, it changed the chemical composition of the glass near the anode. And once the chemistry changed, the glass was more like two different materials, and Joule's law no longer applied uniformly. A hotspot formed.
No one had noticed the effect before, Jain said, likely because it doesn't kick in until the glass is already pretty hot. The material in this experiment didn't develop hotspots until the furnace reached about 600 F (316 C). That's not very hot for glass, but it's much hotter than the conditions under which most electrical machines using glass and electricity work.
For now, though, scientists have figured out why the glass was boiling when it shouldn't have. And that's pretty exciting on its own.
By Rafi Letzter, Live Science
Reality Of Islam |
|
Researchers
A new chip-

A large inf

Choosing th
 9:3:43
9:3:43
 2018-11-05
2018-11-05
10 benefits of Marriage in Islam
 7:5:22
7:5:22
 2019-04-08
2019-04-08
benefits of reciting surat yunus, hud &
 9:45:7
9:45:7
 2018-12-24
2018-12-24
advantages & disadvantages of divorce
 11:35:12
11:35:12
 2018-06-10
2018-06-10
 6:0:51
6:0:51
 2018-10-16
2018-10-16
 12:10:56
12:10:56
 2022-11-17
2022-11-17
 11:11:59
11:11:59
 2023-02-01
2023-02-01
 2:2:13
2:2:13
 2022-10-08
2022-10-08
 8:4:21
8:4:21
 2022-01-08
2022-01-08
 7:45:39
7:45:39
 2018-06-21
2018-06-21
 8:3:0
8:3:0
 2018-06-21
2018-06-21
 7:6:7
7:6:7
 2022-03-21
2022-03-21
 5:41:46
5:41:46
 2023-03-18
2023-03-18
| LATEST |