


 4:57:21
4:57:21  2019-07-17
2019-07-17  1127
1127
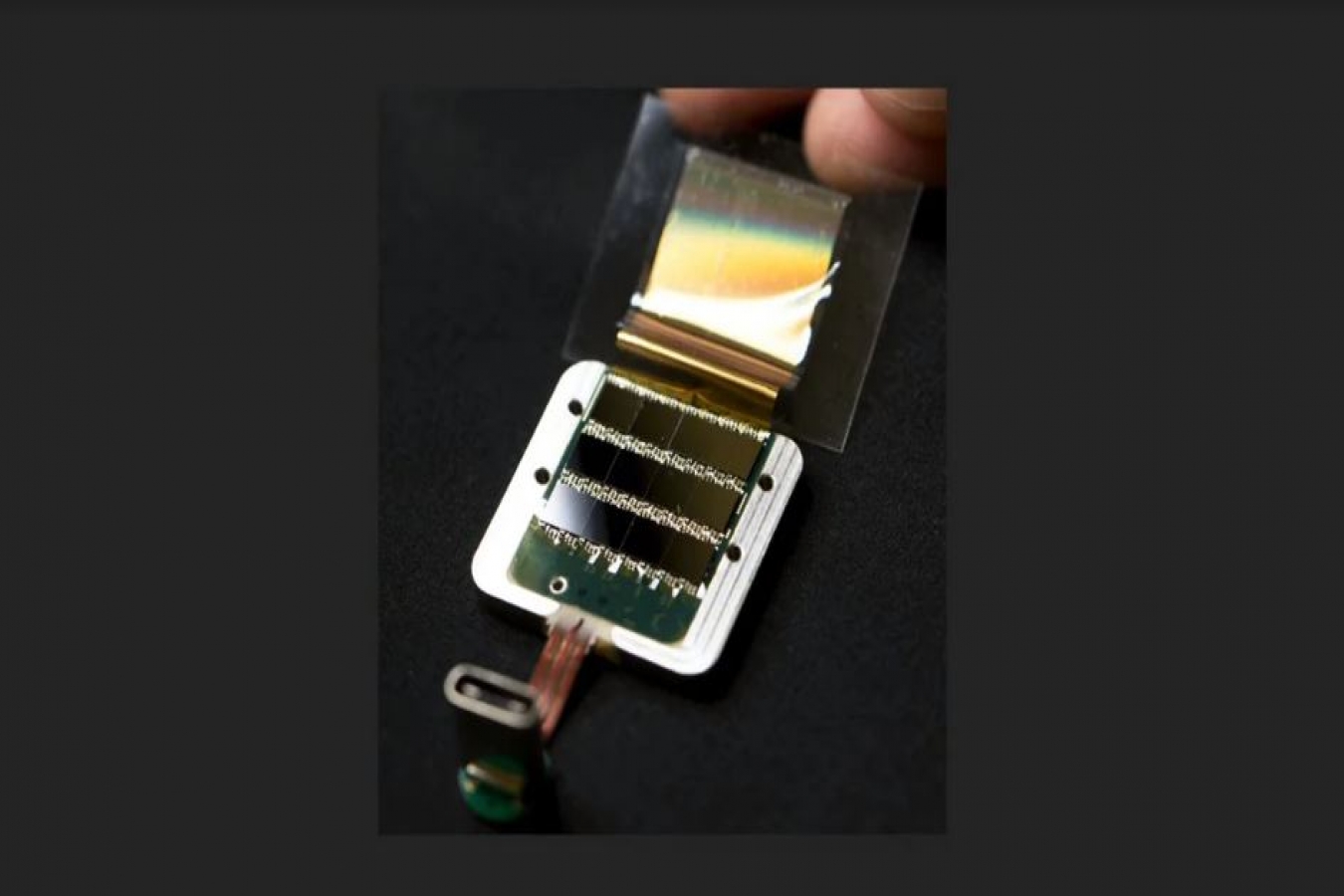

To help paralysed people control devices and empower people with brain disorders enrich their lives, Elon Musk-led startup Neuralink has revealed tiny brain "threads" in a chip which is long-lasting, usable at home and has the potential to replace cumbersome devices currently used as brain-machine interfaces.
The company is seeking the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval to start clinical trials on humans in 2020.
The technology has a module that sits outside the head and wirelessly receives information from "threads" embedded in the brain.
Controlled by an iPhone app, the chip called "N1 sensor" with just a USB port coming out can have as many as 3,072 electrodes per array distributed across 96 "threads" - each "thread" smaller that the tiniest human hair.
The chip which will be wireless in the future can read, transmit high-volume data and amplify signals from the brain. The aim is to drill four 8mm holes into patients' skulls and insert the "threads" each of the size between 4 and 6 micrometre -- about one-third the diameter of a human hair.
Currently, there is a robot to do the brain surgery which, according to a research paper released by Neuralink, has performed surgeries on animals and successfully placed the "threads".
"This has the potential to solve several brain-related diseases. The idea is to understand and treat brain disorders, preserve and enhance your own brain and create a well-aligned future," Musk told the audience at an event here late Tuesday.
A staunch critic of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Musk said that long-term goal is to find a way to "achieve a sort of symbiosis with AI but that is not a mandatory thing. This is something you can choose to have if you want".
"With a high-bandwidth brain-machine interface, I think we can actually help scores of patients," said the Tesla founder who also said he is looking to hire more talent in Neuralink.
According to Max Hodak, President of Neuralink, he wasn't originally sure "this technology was a good idea" but Musk convinced him.
"We didn't want any connectors or wires coming through the skin. It had to be something that would last for a longer period of time, not something that you'd have to take out after two-three years; it had to have practical bandwidth," said Hodak.
Founded as a medical research company in 2016, Neuralink has hired several high-profile neuroscientists from various universities.
The company is focused on creating devices resembling tiny sewing machines that can be implanted in the human brain - to improve memory or more direct interfacing with computing devices.
Reality Of Islam |
|
A new study
Researchers
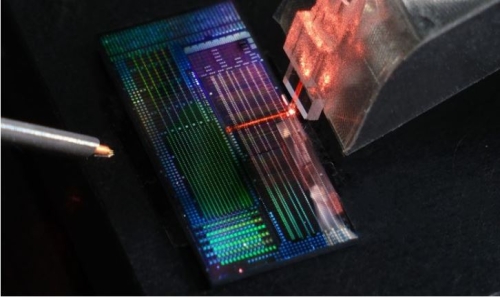
A new chip-

A large inf
 9:3:43
9:3:43
 2018-11-05
2018-11-05
10 benefits of Marriage in Islam
 7:5:22
7:5:22
 2019-04-08
2019-04-08
benefits of reciting surat yunus, hud &
 9:45:7
9:45:7
 2018-12-24
2018-12-24
advantages & disadvantages of divorce
 11:35:12
11:35:12
 2018-06-10
2018-06-10
 6:0:51
6:0:51
 2018-10-16
2018-10-16
 10:55:53
10:55:53
 2022-06-13
2022-06-13
 8:3:0
8:3:0
 2018-06-21
2018-06-21
 1:38:41
1:38:41
 2021-12-08
2021-12-08
 12:47:1
12:47:1
 2022-12-20
2022-12-20
 11:34:48
11:34:48
 2022-06-29
2022-06-29
 7:34:7
7:34:7
 2023-02-28
2023-02-28
 2:2:13
2:2:13
 2022-10-08
2022-10-08
 5:41:46
5:41:46
 2023-03-18
2023-03-18
| LATEST |