
CATECHOLAMINES AS NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 المؤلف:
James R Hanson
المؤلف:
James R Hanson
 المصدر:
Chemistry and Medicines
المصدر:
Chemistry and Medicines
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 54
الجزء والصفحة:
p 54
 8-10-2017
8-10-2017
 1828
1828
CATECHOLAMINES AS NEUROTRANSMITTERS
There are three neurotransmitters that are derived from the amino acid L-tyrosine 3.30 (see Scheme 5). They are dopamine (dihydroxyphenylethylamine) 3.4, noradrenalin 3.2 and adrenalin 3.3. Both noradrenalin and adrenalin are chiral alcohols and it is the R enantiomer that is active. They are found in both the peripheral nervous system and the CNS.

Scheme 5 The formation of the catecholamines
The biosynthesis of these compounds involves the hydroxylation of Ltyrosine 3.30 to L-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) 3.31, decarboxylation to form dopamine 3.4, hydroxylation to form noradrenalin 3.2 and finally N-methylation to give adrenalin 3.3. The first step in this sequence is rate-limiting. Once the compounds have been formed, they are stored in the nerve endings prior to their release.
While dopamine 3.4 and noradrenalin 3.2 are localized in their action, adrenalin 3.3 is also a circulatory hormone produced by the adrenal glands.
The hormones are metabolized by the monoamine oxidase pathway, which converts the compounds via their imines to the aldehydes and which are then oxidized to the acids e.g. 3.32. There are two forms of monoamine oxidase. Monoamine oxidase A metabolizes noradrenalin and serotonin while dopamine is metabolized by monoamine oxidase B. Another metabolic pathway involves the COMT system, which converts the phenolic hydroxyl group that is meta to the side chain, to a methoxyl, e.g. 3.33. The methyl ether may then be metabolized via the monoamine oxidase pathway to a hydroxy-acid. The compounds may also be excreted as their sulfates. These metabolic changes prevent the neurotransmitter from binding to its receptor. A regulatory mechanism involves the re-uptake of noradrenalin. This leads to the inhibition of its release and thus it provides a negative feedback regulation.
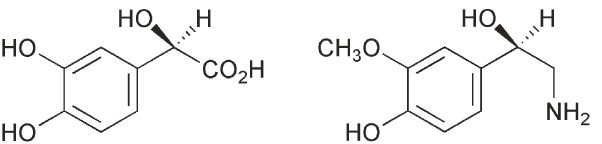
3.32 3.33
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


