


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 31-8-2017
Date: 5-9-2017
Date: 22-8-2017
|
Production of Chloromethanes
Methane is the most difficult alkane to chlorinate. The reaction is initiated by chlorine free radicals obtained via the application of heat (thermal) or light (hv). Thermal chlorination (more widely used industrially) occurs at approximately 350–370°C and atmospheric pressure. A typical product distribution for a CH4/Cl2 feed ratio of 1.7 is: mono- (58.7%), di-(29.3%) tri- (9.7%) and tetra- (2.3%) chloromethanes.
The highly exothermic chlorination reaction produces approximately 95 KJ/mol of HCI. The first step is the breaking of the Cl–Cl bond (bond energy = + 584.2 KJ), which forms two chlorine free radicals (Cl atoms):

The Cl atom attacks methane and forms a methyl free radical plus HCI. The methyl radical reacts in a subsequent step with a chlorine molecule, forming methyl chloride and a Cl atom:

The new Cl atom either attacks another methane molecule and repeats the above reaction, or it reacts with a methyl chloride molecule to form a chloromethyl free radical .CH2Cl and HCl.
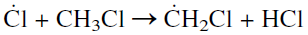
The chloromethyl free radical then attacks another chlorine molecule and produces dichloromethane along with a Cl atom:
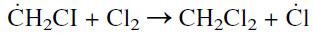
This formation of Cl free radicals continues until all chlorine is consumed.
Chloroform and carbon tetrachloride are formed in a similar way by reaction of C˙HCl2 and C˙Cl3 free radicals with chlorine. Product distribution among the chloromethanes depends primarily on the mole ratio of the reactants. For example, the yield of monochloromethane could be increased to 80% by increasing the CH4/Cl2 mole ratio to 10:1 at 450°C. If dichloromethane is desired, the CH4/Cl2 ratio is lowered and the monochloromethane recycled. Decreasing the CH4/Cl2 ratio generally increases polysubstitution and the chloroform and carbon tetrachloride yield.
An alternative way to produce methyl chloride (monochloromethane) is the reaction of methanol with HCl (see later in this chapter,
“Chemicals from Methanol”). Methyl chloride could be further chlorinated to give a mixture of chloromethanes (dichloromethane, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride).



|
|
|
|
مخاطر خفية لمكون شائع في مشروبات الطاقة والمكملات الغذائية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"آبل" تشغّل نظامها الجديد للذكاء الاصطناعي على أجهزتها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلميّ يُواصل عقد جلسات تعليميّة في فنون الإقراء لطلبة العلوم الدينيّة في النجف الأشرف
|
|
|