


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 29-8-2017
Date: 5-9-2017
Date: 22-8-2017
|
Alkylation Process
Alkylation in petroleum processing produces larger hydrocarbon molecules in the gasoline range from smaller molecules. The products are branched hydrocarbons having high octane ratings.
The term alkylation generally is applied to the acid catalyzed reaction between isobutane and various light olefins, and the product is known as the alkylate. Alkylates are the best of all possible motor fuels, having both excellent stability and a high octane number.
Either concentrated sulfuric acid or anhydrous hydrofluoric acid is used as a catalyst for the alkylation reaction. These acid catalysts are capable of providing a proton, which reacts with the olefin to form a carbocation.
For example, when propene is used with isobutane, a mixture of C5 isomers is produced. The following represents the reaction steps:

The formed carbocation from the last step may abstract a hydride ion from an isobutane molecule and produce 2,2-dimethylpentane, or it may rearrange to another carbocation through a hydride shift.

The new carbocation can rearrange again through a methide/hydride shift as shown in the following equation:
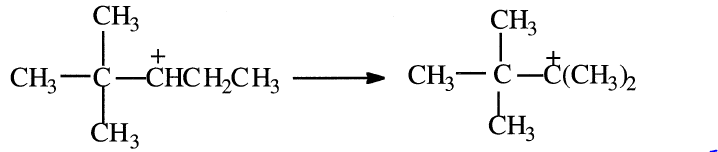
The rearranged carbocation finally reacts with isobutane to form 2,2,3- trimethylbutane.
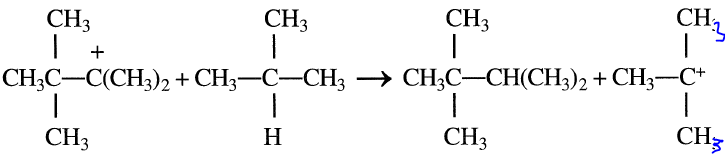
The final product contains approximately 60–80% 2,2-dimethylpentane and varying amounts of 2,2,3-trimethylbutane and 2-methylhexane. The primary process variables affecting the economics of sulfuric acid alkylation are the reaction temperature, isobutane recycle rate, reactor space velocity, and spent acid strength. To control fresh acid makeup, spent acid could be monitored by continuously measuring its density, the flow rate, and its temperature. This can reduce the acid usage in alkylation units.
The presence of impurities such as butadiene affects the product yield and properties. Butadiene tends to polymerize and form acid-soluble oils, which increases acid makeup requirements. For every pound of butadiene in the feed, ten pounds of additional make-up acid will be required.35 Other olefins that are commercially alkylated are isobutene and 1- and 2 butenes. Alkylation of isobutene produces mainly 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (isooctane).
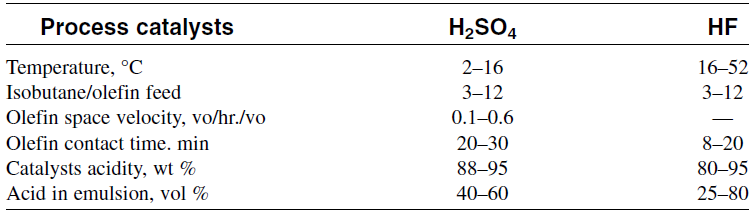
Both sulfuric acid and hydrofluoric acid catalyzed alkylations are low temperature processes. Table 1.1 gives the alkylation conditions for HF and H2SO4 processes.
Table 1.1: Ranges of operating conditions for H2SO4 and HF alkylation
One drawback of using H2SO4 and HF in alkylation is the hazards associated with it. Many attempts have been tried to use solid catalysts such as zeolites, alumina and ion exchange resins.
Also strong solid acids such as sulfated zirconia and SbF5/sulfonic acid resins were tried. Although they were active, nevertheless they lack stability. No process yet proved successful due to the fast deactivation of the catalyst. A new process which may have commercial possibility, uses liquid trifilic acid (CF3-SO2OH) on a porous solid bed. Using isobutane and light olefins, the intermediates are: isopropyl, sec-butyl, 2-pentyl, and 3-pentyl esters of trifilic acid.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|