
Cracking Process
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 76
الجزء والصفحة:
p 76
 24-7-2017
24-7-2017
 1857
1857
Cracking Process
Most catalytic cracking reactors are either fluid bed or moving bed. In the more common fluidized bed process (FCC), the catalyst is an extremely porous powder with an average particle size of 60 microns. Catalyst size is important, because it acts as a liquid with the reacting hydrocarbon mixture. In the process, the preheated feed enters the reactor section with hot regenerated catalyst through one or more risers where cracking occurs. A riser is a fluidized bed where a concurrent upward flow of the reactant gases and the catalyst particles occurs. The reactor temperature is usually held at about 450–520°C, and the pressure is approximately 10–20 psig. Gases leave the reactor through cyclones to remove the powdered catalyst, and pass to a fractionator for separation of the product streams. Catalyst regeneration occurs by combusting carbon deposits to carbon dioxide and the regenerated catalyst is then returned to the bottom of the riser. Figure 1.1 is a typical FCC reactor/regeneration system.

Figure 1.1. Typical FCC reactor/regenerator
Fluid catalytic cracking produces unsaturates, especially in the light hydrocarbon range C3–C5, which are used as petrochemical feedstocks and for alkylate production. In addition to hydrocarbon gases, FCC units produce gasolines with high octane numbers (due to the high aromatic content, branched paraffins and olefins), gas oils, and tar. The ratio of
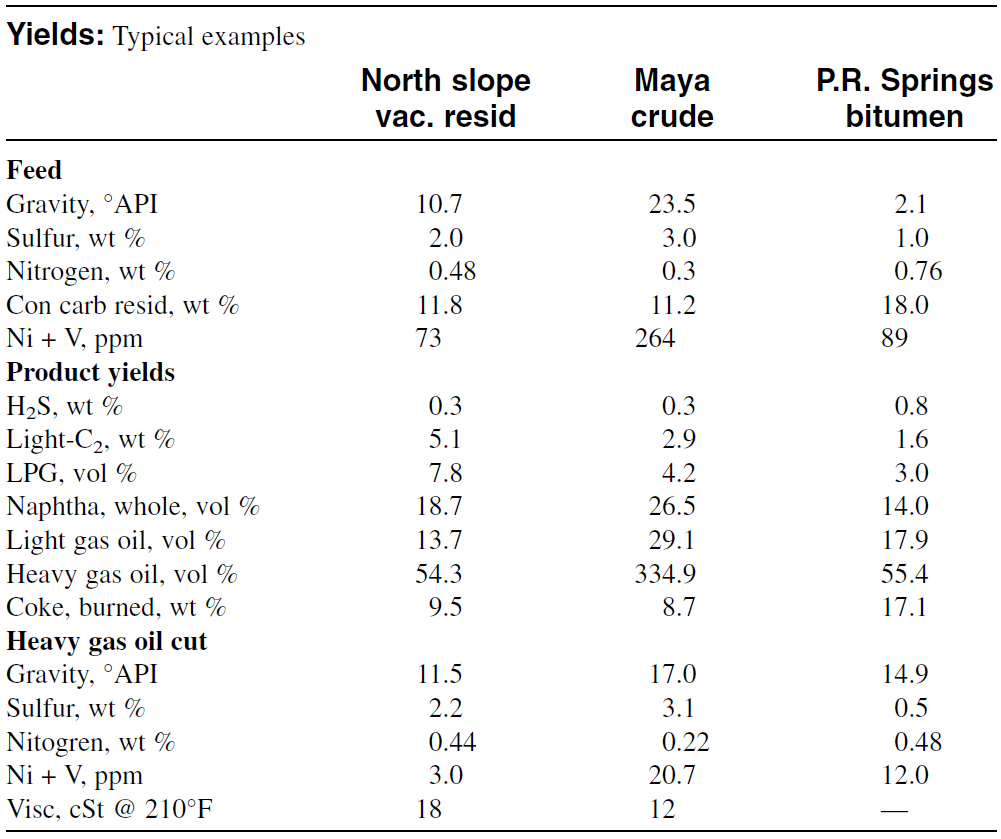
these products depends greatly on the different process variables. In general, higher conversions increase gas and gasoline yields. Higher conversion also increases coke formation. Process variables that increase conversion are higher temperatures, longer residence times, and higher catalyst/oil ratio. Table 1.1 shows the analysis of the feed and the products rom an FCC unit.
In the moving bed processes, the preheated feed meets the hot catalyst, which is in the form of beads that descend by gravity to the regeneration zone. As in fluidized bed cracking, conversion of aromatics is low, and a mixture of saturated and unsaturated light hydrocarbon gases is produced. The gasoline product is also rich in aromatics and branched paraffins.
Table 1.1:Analysis of feed and products from a fluid catalytic cracking process
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


