

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Strengths of Acids and Bases
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المصدر:
College Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 116
17-7-2017
2747
Strengths of Acids and Bases
The equilibria of Eqs. (1-1) and (1-2) correspond to the equilibrium constant expressions:
 (1.1)
(1.1)
 (1.2)
(1.2)
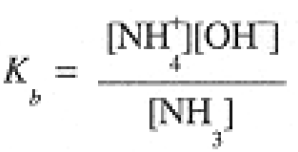 (1.3)
(1.3)
 (1.4)
(1.4)
These expressions are often written in logarithmic form:
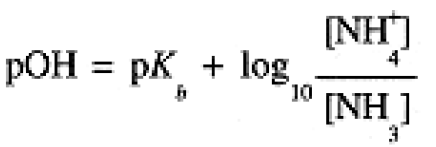 (1.5)
(1.5)
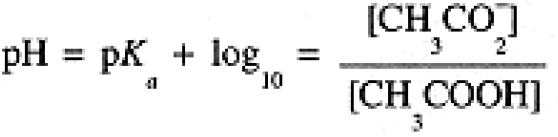 (1.6)
(1.6)
We can also think of NH4+ as an acid, so that in solutions of NH4Cl, we have the equilibrium

 (1.7)
(1.7)
Adding eqs (1-5) and (1-7), we have
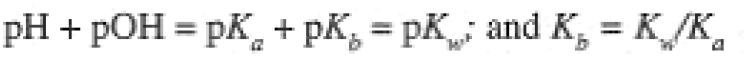 (1.8)
(1.8)
Equation (1-8) is a general result relating pKa of an acid with pKb of the conjugate base. The value of Ka or Kb (pKa or pKb) determines the extent of ionization of an acid or base. We think of strong acids or bases as completely ionized (or nearly so). This generally implies Ka or Kb greater than 1 (negative pKa or pKb). The pKa values for several acids are given in Table 1.1.
Many common acids are oxoacids, i.e., molecules with the central atom surrounded by =O (oxo) and –OH (hydroxo) groups. Perchloric (HClO4), chloric (HClO3), chlorous (HClO2), and hypochlorous (HClO) acids can be written ClO3OH), ClO2(OH), ClO(OH), and ClOH, respectively, to emphasize the distinction between oxo and hydroxo oxygens. The acid strength increases with the number of oxo O's. The increased acidity results from the delocalization of negative charge in the anions as shown in Figure 1.1 for the Cl oxoanions. The average formal charge on oxygen is -1/4 in ClO4-, -1/3 in ClO3-, -1/2 in ClO2-, and -1 in ClO-.
Table 1.1. pKa's of Some Common Acids

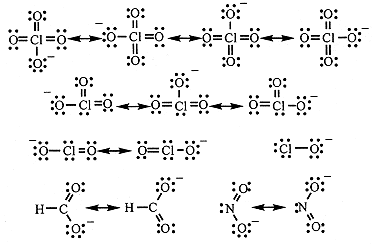
Figure 1.1. Resonance structures of the perchlorate, chlorate, chlorite, hypochlorite, formate, and nitrite ions.
Five of the acids listed in Table 1.1 are polyprotic acids, i.e., acids with more than one acidic H. Forexample, phosphoric acid ionizes in three steps:

The acidity of the neutral acid is in the range expected for an oxoacid with one oxo O. In the second and third steps, phosphoric acid is a much weaker acid. In general, we find that pKa increases by about 5 for each successive ionization step for a polyprotic acid. An exception to this rule is oxalic acid, H2C2O4 = HOOCCOOH, where the acidic -OH groups are bound to different C atoms and behave more nearly independently.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















