

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Chemical Formulas from Mass Spectrometry
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المصدر:
College Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 17
24-6-2017
2359
Chemical Formulas from Mass Spectrometry
The molecular mass of a compound is the average mass (in u) of a molecule, weighted among the various isotopic forms (isotopomers) of the different component elements. A nuclidic molecular mass may be defined for a molecule made up of particular nuclides by adding nuclidic atomic masses in the same way that the molecular mass is computed from average atomic masses.
A mass spectrometer is an instrument that separates particles by mass and measures their individual relative masses. If a nuclidic mass of an unknown compound is known with great precision from mass spectrometry, the exact molecular formula can often be deduced directly from this information without resort to a quantitative chemical analysis.
Example 1
Consider carbon monoxide, CO, dinitrogen, N2, and ethylene, C2H4. The masses and fractional abundances of some isotopic forms of these molecules are listed in Table 1.1 (isotopic forms not listed have abundances less than 0.0001 or 0.01%). Since 12C, 16O, 14N, and 1H are by far the most abundant isotopes of C, O, N, and H, a particle of mass number 28 will be detected in all three cases. With a mass spectrum, Figure 1-1, the three gases can be distinguished on the basis of their nuclidic masses. The mass 29 and 30 satellites provide confirmation of the assignment.
Table 1.1
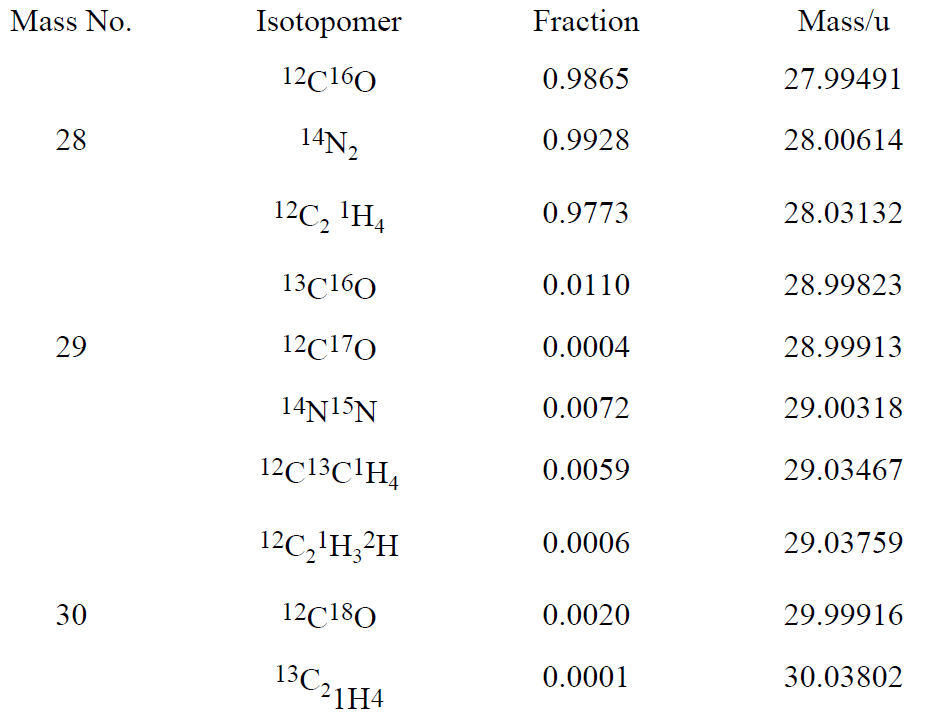
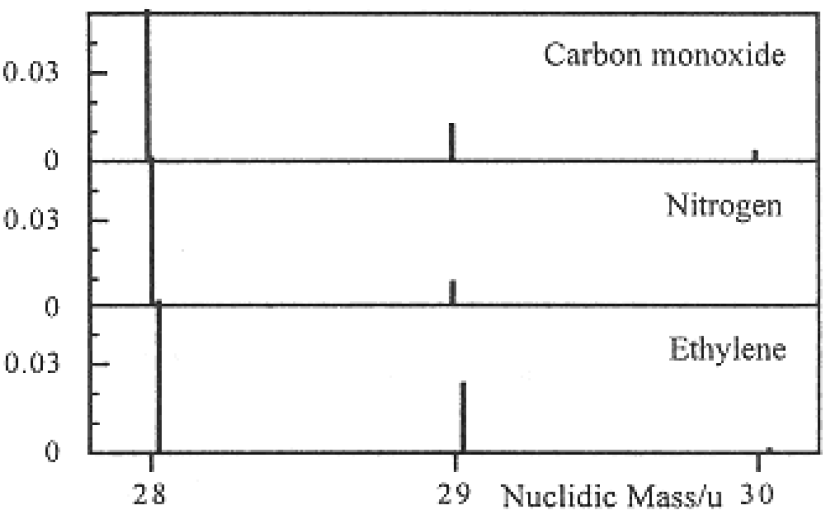
Figure 1-1. Mass spectra of CO, N2, and C2H4. Note that the major peak at mass 28 has been truncated.
Example 2
Find the formula of an organic compound whose dominant nuclidic species has a precise nuclidic molecular mass of 44.025 u, given that no other elements than C, H, O, and N are present and only 12C, 1H, 16O, and 14N are involved.
Considering all possible combinations of C, H, O, and N, we find six molecular formulas with nuclidic molecular masses of about 44. These are listed in Table 1.2 with nuclidic molecular masses.
Table 1.2
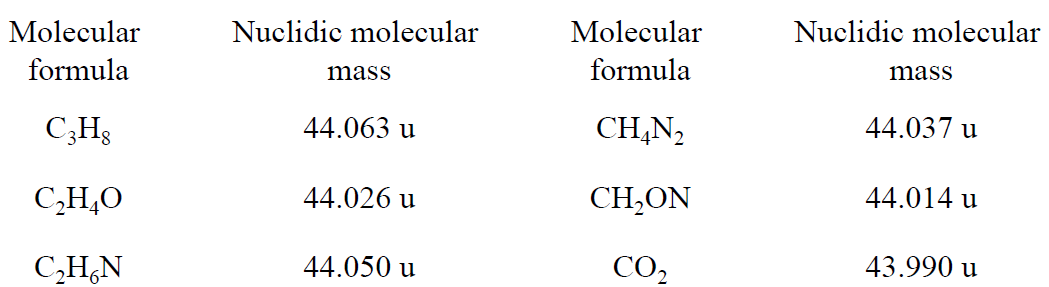
When these nuclidic masses are compared with the experimental value, 44.025 u, C2H4O is the only formula that fits the data within the claimed precision; so this must be the formula of the compound.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















